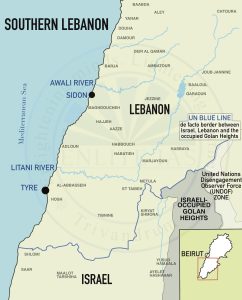
Syrian Conflict (2011 – Present)
- Location: West Asia near Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant.
- Nature of Conflict: Multi-sided civil war and proxy war
- Reasons
- Authoritarian rule under Bashar al-Assad
- Arab Spring protests met with violent repression
- Sectarian divide (Alawite-led regime vs Sunni majority)
- Economic distress, drought, and unemployment.
- Parties Involved
- Government: Assad regime, Syrian Arab Army
- Opposition: Free Syrian Army, Islamist rebel groups
- Extremists: ISIS, Al-Qaeda affiliates
- Kurds: YPG / Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF)
- External Powers: Russia, Iran, Turkey, USA, Gulf states
- Current Status: Ended in December 2024 with the fall of Bashar al-Assad and the collapse of the Baathist regime, following nearly 61 years of rule. A rebel coalition led by Hay’at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) seized Damascus.
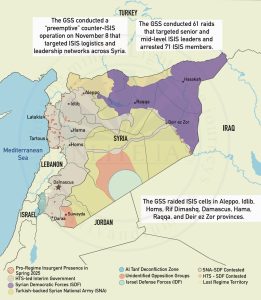
Israel–Gaza Strip War
- Location: West Asia in the Mediterranean Coast
- Reasons
- Gaza has been under an Israeli–Egyptian blockade since 2007 after Hamas takeover
- Long-standing Israel–Palestine conflict (territory, security, statehood)
- Immediate cause: Large-scale Hamas attack on Israel (Oct 2023)
- Parties Involved
- Israel: IDF (air, ground, naval operations)
- Hamas: Rockets, tunnels, guerrilla tactics
- Others: Palestinian Islamic Jihad; regional spillover involving Hezbollah (Lebanon border) and Houthis (Yemen).
- Diplomacy by: Egypt, Qatar, US
- Present Status: Fighting and localized pauses/ceasefire talks recur intermittently
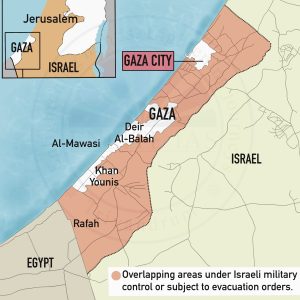
Yemen Civil War (2014 – Present)
- Location: West Asia border Red Sea, Persian Gulf and Indian Ocean
- Nature: Civil War and Proxy War
- Causes
- Political transition failure after Arab Spring (2011)
- Marginalisation of Houthis and weak central authority
- Sectarian and tribal rivalries
- Regional rivalry (Iran–Saudi) is turning Yemen into a proxy battleground
- Parties Involved
- Houthis (Ansar Allah): Zaydi Shia rebels; control Sana’a and north-west
- Internationally Recognised Government: Backed by Saudi-led coalition
- Saudi-led Coalition: Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates
- External Backers: Iran (Houthis), United States (coalition support)
- Others: Southern Transitional Council (STC), AQAP, ISIS (limited)
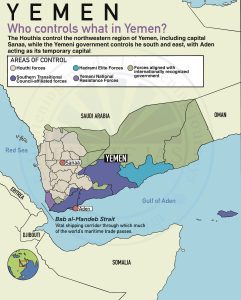
Israel–Lebanon Conflict
- Location: West Asia
- Context: Longstanding disputes over territory, including the Shebaa Farms area.
- Causes:
- Territorial disputes between the parties.
- Proxy wars involving Hezbollah in the region.
- Spillover from the Gaza conflicts.
- Parties Involved
- Israel: IDF (air, ground, naval operations)
- Hezbollah is an Iran-backed non-state actor present in Lebanon, claiming solidarity with Gaza and Palestine.
- Facts: The Israel-Lebanon boundary is demarcated by the Blue Line- The UN-verified demarcation.