Definition
- Violent shaking of earth due to release of energy , generating seismic waves in all direction.
Earthquake Waves
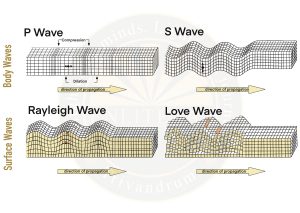
- Body Waves: Move in all direction travelling through the body of the earth
- P Waves: Move faster. First to report on the surface of earth. Similar to sound wave and travel in all 3 medium
- S Waves: Arrive with some time lag and travel only trough solid material.
- Surface Waves: Last to report on seismograph and mor destructive.
- Rayleigh Waves: A Rayleigh wave is a seismic surface wave that causes an oval shudder with no transverse or perpendicular motion. They behave like water waves.
- Love Waves: A seismic surface wave caused by the horizontal movement of the earth during an earthquake is known as a love weave.
Associated Terms
- Hypocentre: Location where an earthquake starts just below earth’s surface.
- Focus: Location right above the hypocentre on the earth’s surface.
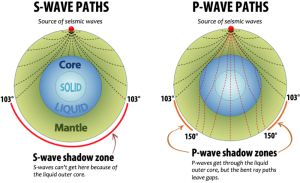
Shadow Zone
Causes of Earthquake
- Faulting
- Tectonic movements
- Volcanic eruptions
- Human activities like nuclear explosion, and mining.
Measuring of Earthquakes
- Richter Scale: Based on magnitude.
- Mercalli Scale: Based on intensity
World Distribution of Earthquakes
- About 70% of earthquakes occur in the Circum-Pacific belt as the epicentre and the most frequent occurrences are along the ‘Pacific Ring of Fire’.
- Another 20% of earthquakes take place in the Mediterranean-Himalayan belt including Asia Minor, the Himalayas, and parts of north-west China.

Consequences of Earthquakes
- Collapse of Human Property and Loss of Life
- The deformation of the ground surface because of the vertical and horizontal movement of the earth’s crust causes huge damage and destruction to human establishments and structures.
- For example – Syria – Turkey earthquake (2023) due to the movement of the Anatolian plate.
- Landslides and Avalanches
- Tremors especially in mountain areas can cause slope instability and slope failure leading to fall of debris down the slope causing landslides.
- The huge masses of ice may fall down snow-covered peaks due to earthquakes causing Avalanches.
- For Example: – Nepal earthquake (2015)
- Floods
- The earthquake can lead to devastating disturbances to dams, reservoirs and can cause flash floods.
- For example – The Kakhovka Dam in Ukraine was breached in the early hours of 6 June 2023, causing extensive flooding along the lower Dnieper river.
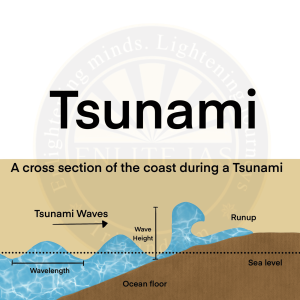
- Tsunami
- A tsunami is a set of waves created by a disturbance, likely an earthquake, which reaches the surface of the sea.
- For example: – The Tsunami of 26th December 2004 of the Indian Ocean was caused by an earthquake off the coast of Sumatra.
- Note – Other causes of tsunami are volcanic eruption, underwater nuclear explosion, and landslides.