Division of Banks
Scheduled Banks
- Scheduled Banks under the Banking System in India refer to those financial institutions that are listed in the 2nd Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- Conditions:
- It should have paid-up capital and reserves of not less than 5 lacs, and
- It should satisfy the RBI that their affairs are not being conducted in a manner detrimental to the interest of their depositors.
- Types:
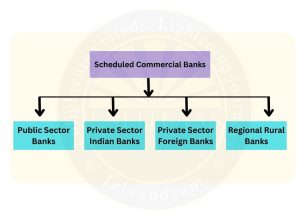
-
Public Sector Banks (PSBs)
- Public Sector Banks (PSBs) are also known as Nationalised Banks.
- They refer to those financial institutions under the Banking System in India where the majority ownership, i.e. more than 50% of the shares, lies with the government.
- For example – State Bank of India , Indian Overseas Bank (IOB)
-
Private Sector Banks
- Private Sector Banks are those banks under the Indian Banking System in which the private sector has a shareholding of more than 51%. For example, the ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, etc.
-
Foreign Banks
- Foreign Banks refer to those banks that have their headquarters in a different country but operate branches or subsidiaries within India. For example, HSBC, Citi Bank, etc.
-
Regional Rural Banks (RRB)
- RRBs are government-owned scheduled commercial banks of India that operate at the regional level in different states of India.
- They serve the country’s rural areas and provide them with basic banking and other financial-related services.
- Origin:
- The Narasimham Committee on Rural Credit (1975) recommended the establishment of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs).
- The establishment of RRBs finds its route in the ordinance passed on 26th September 1975 and the RRB Act 1976.
- Prathama Grameen Bank was the first RRB bank and was established on 2nd October 1975.
- Functions:
- To provide basic banking facilities to rural and semi-urban areas.
- To effect some governmental functions, such as the disbursal of wages under the MGNREGA policy.
- To provide other bank-related facilities such as locker facility, internet banking, mobile banking, debit and credit cards, etc.
- Grant credit facilities to people in rural areas, such as small farmers, artisans, small entrepreneurs, etc.
- To accept deposits from people.
- Regulation: Regional Rural Banks are regulated by RBI and supervised by the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD).
- Ownership: RRBs are jointly owned by the Government of India (GOI), the Sponsor Bank and the concerned State Government with share proportions of 50%, 35% & 15%, respectively.
- Management: The Board of Directors manages these banks, overall affairs, which consists of one Chairman, three Directors as nominated by the Central Government, a maximum of two Directors as nominated by the concerned State Government, and a maximum of three Directors as nominated by the sponsor bank.
