Development
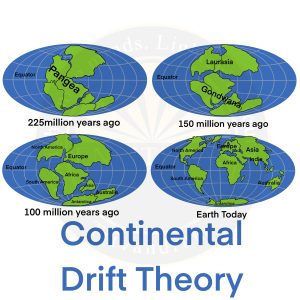
- Continental Drift theory was put forth by Alfred Wegener in 1912.
- According to Wegener, all the continents formed a single continental mass which is called “Pangaea” and this supercontinent was surrounded by a mega ocean called “Panthalassa ”.
- Later the supercontinent Pangea split into two – Laurasia in the north and Gondwanaland in the south.
- Gondwanaland consisted of Antarctica and was joined to South America, Africa, India, and Australia.
- Laurasia consisted of North America, Greenland, and all of Eurasia.
- Subsequently, Laurasia and Gondwanaland continued to break into various smaller continents that exist today.
Forces Responsible for Continental Drift
- Based on Direction
- Towards the Equator – Due to the interaction of forces of gravity, pole-fleeing force and buoyancy.
- Westwards – Due to tidal currents because of the earth’s motion.
Evidence in Support of the Continental Drift Theory
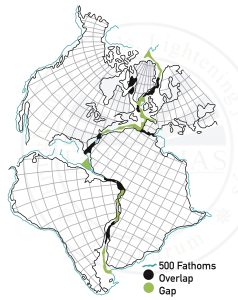
- Jig-Saw-Fit
- The similarity in outline of the coastlines of eastern South America and West Africa.
- Similarly, when matched, Africa, Madagascar, and India’s east coast all fit together.
- Geological Structure
- The Appalachian mountains of North America which come right up to the coast and continue their trend across the ocean in the old Hercynian Mountains of southwest Ireland, Wales, and central Europe.
- The opposite coasts of Africa and Brazil display even greater resemblance in their structure and rocks. For example, the gold deposit in Ghana (Africa) traces its origin to Brazil.
- Coal deposits have been found in temperate and polar regions; however, coal is formed in tropical regions.
- Glacial Deposits
- Glacial deposits formed during the Permo-Carboniferous glaciation (about 300 million years ago) are found in Antarctica, Africa, South America, India and Australia.
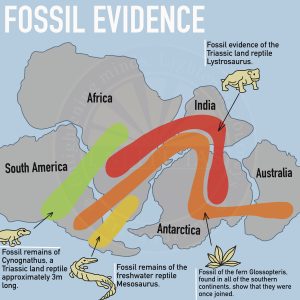
- Fossil Evidence
- Fossils of identical species and animals were found on both sides of the marine barrier.
- For example, Mesosaurus, a freshwater crocodile-like reptile that lived between 286 and 258 million years ago, is only found in Southern Africa and Eastern South America.
Criticism of Continental Drift Theory
- Wegener failed to explain why the drift began only in the Mesozoic era and not before.
- The theory doesn’t consider the formation of islands and mountains.
- Proofs heavily depend on assumptions that are generalist.
- The evolution of species may occur simultaneously in different places.
- Forces like buoyancy, tidal currents, and gravity are too weak to be able to move continents.
- As per theory sial is floating over Sima but in reality, the lithosphere is floating on the asthenosphere.
