Why in the news?
- India launched the first indigenous CRISPR-based Gene therapy, BIRSA 101, to treat Sickle Cell Disease.
BIRSA 101
- What is it?: BIRSA 101 is a tribal health initiative launched by the Government of India to eliminate Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) among tribal and other high-risk populations.
- Launch: Announced in Union Budget 2023–24 and launched in 2023, as part of the broader National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission (NSCAEM) 2047
- Full Form:
- BIRSA: Blood Initiative for Rapid Screening Action.
- 101 refers to a standardised screening protocol designed for large-scale, last-mile detection.
- Objectives:
- Early detection of SCD among tribal youth, children, and pregnant women.
- Mass screening in high-prevalence states (Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, MP, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Gujarat).
- Counselling and genetic awareness to reduce disease transmission.
- Strengthen primary health care and digital tracking of patients.
- Key Features:
- Door-to-door screening using a simple card-based test and confirmatory lab diagnostics.
- Integration with ABHA Health ID and Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
- Mandatory pre-marital and antenatal screening campaign in high-incidence districts.
- ASHA, ANM, Tribal Health Workers as field personnel.
- Focus on tribal communities, where SCD prevalence can be 10–15% for carriers and 1–2% for disease.
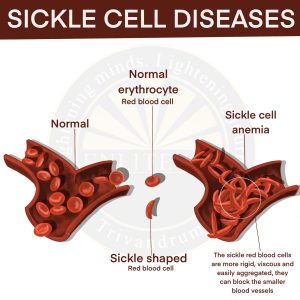
Sickle Cell Disease
- What is it? – It is an inherited blood disorder.
- Effect
- It affects hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells that delivers oxygen to cells throughout the body.
- People with this disease have atypical hemoglobin molecules called hemoglobin S, which can distort red blood cells into a sickle, or crescent, shape.
- What causes it? – The cause of Sickle cell disease is a defective gene, called a sickle cell gene.
- Symptoms:
- Early stage: Extreme tiredness or fussiness from anemia, painfully swollen hands and feet, and jaundice.
- Later stage: Severe pain, anemia, organ damage, and infections.
- Diagnosis
- Solubility test / Dithionite test
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis
- HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography)
- Genetic testing (for prenatal diagnosis)
- Treatments – The only cure for this disease is bone marrow or stem cell transplantation.
Sickle Cell Disease in India
- Area Affected: High prevalence in Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, MP, Maharashtra, Gujarat and Rajasthan.
- Government Initiatives to Counter
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission (NSCAEM), 2023–2047: Aiming to Screen 7 crore people aged 0–40 years in high-burden states and ensure genetic counselling and follow-up care.
- BIRSA 101: Rapid, decentralised screening model.
- Tribal Health Action Plan: Special focus on PVTGs under PM-JANMAN & TB-Mukt Bharat convergence.
Source: Indian Express
