Basic Concepts of National Income
- National Income – It refers to the aggregate value of all the final goods and services produced in a country in a particular period of time (usually one financial year).
- National Income Accounting – This is a bookkeeping system that a national government uses to measure the level of the country’s economic activity in a given time period.
Basic Concepts Related to National Income Accounting
- Circular Flow of Income: The circular flow of income is a model of the economy in which major exchanges are represented as flows of money, goods, services, etc. among the economic agents. As per this model, money and goods & services flow in the opposite direction but move in a closed circuit.
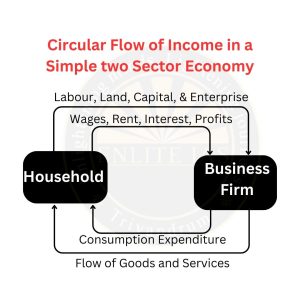
- Domestic/ Economic Territory: It refers to the geographical territory administered by the Government of India within which the person, goods, and capital can circulate freely.
- Market Price (MP):
- Market Price (MP) refers to the price that a consumer pays for the product while purchasing it from the seller.
- Market Price (MP) includes indirect taxes (as they are added to the selling price) and excludes subsidies received (as they are deducted from the selling price).
- Factor Cost (FC):
- Factor Cost (FC) refers to the cost of factors of production that are incurred by a firm when producing goods and services.
- Factor Cost (FC) = Market Price – Indirect Taxes + Subsidy
- Nominal Price or Current Price:
- The market price of any good or service in the current year is called the Nominal Price or Current Price.
- Inflation is included in the current market price, the Nominal Price or Current Price changes as per the current level of inflation.
- Constant Price:
- Constant price series are used to measure the true volume growth, i.e. adjusting for the effects of price inflation.
- It is calculated on base year.
- Depreciation: Depreciation, also known as the Consumption of Fixed Capital, refers to the loss in value of fixed assets due to wear and tear, accidental damages, and obsolescence.
- Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA):
- Net factor income from abroad is the difference between factor income earned abroad by the residents of a country and factor income earned in that country’s domestic territory by non-residents.
- Labor, land, capital, and enterprise are the four factors of production in economic theory.
- Each of these factors receives a return on its investment in production, which is referred to as Factor Income.
- It is defined by the CSO as “income attributable to factor services rendered by ordinary residents of the country to the rest of the world, minus factor services rendered to them by the rest of the world.”
- Its three main components are as follows:
- Net compensation of employees.
- Net income from property and entrepreneurship (rent, interest, profit).
- Net retained earnings of resident companies abroad.
- It should be noted that net factor income from abroad can be both positive and negative. This is negative when foreigners’ income from our country exceeds our income from abroad, and positive when the former exceeds the latter.
- Transfer Payments:
- Transfer Payments refer to those unilateral payments corresponding to which there is no exchange of goods or services.
- Examples: scholarships, gifts, donations, etc.
- Transfer payments are not included in National Income (NI).
- Capital Output Ratio (COR):
- Capital Output Ratio (COR) refers to the amount of capital (investment) needed to produce one unit of output.
- Capital Output Ratio (COR) reflects the level of efficiency in an economy. The higher the COR, the more capital is required to produce, and hence less efficiency is there in the economy, and vice versa.
- Incremental Capital Output Ratio (ICOR):
- Incremental Capital Output Ratio (ICOR) refers to the additional unit of capital (investment) needed to produce an additional unit of output.

