Environment
Ecology: Ecological Efficiency
Ecological efficiency describes the efficiency with which energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next. The number of trophic levels in the grazing food chain is restricted as the transfer of energy follows 10 percent law – only … Continue reading
Ecology: Ecological Pyramids
What is an Ecological Pyramid? Ecological Pyramid is a graphical depiction which is meant to illustrate the relationship between different living organisms at different trophic levels in an ecosystem Each of the bars that make up the pyramid represents a … Continue reading
Ecology: Food Web
Multiple interlinked food chains make a food web. Food web represents all the possible paths of energy flow in an ecosystem. The food web provides more than one alternative for food to most of the organisms in an ecosystem and … Continue reading
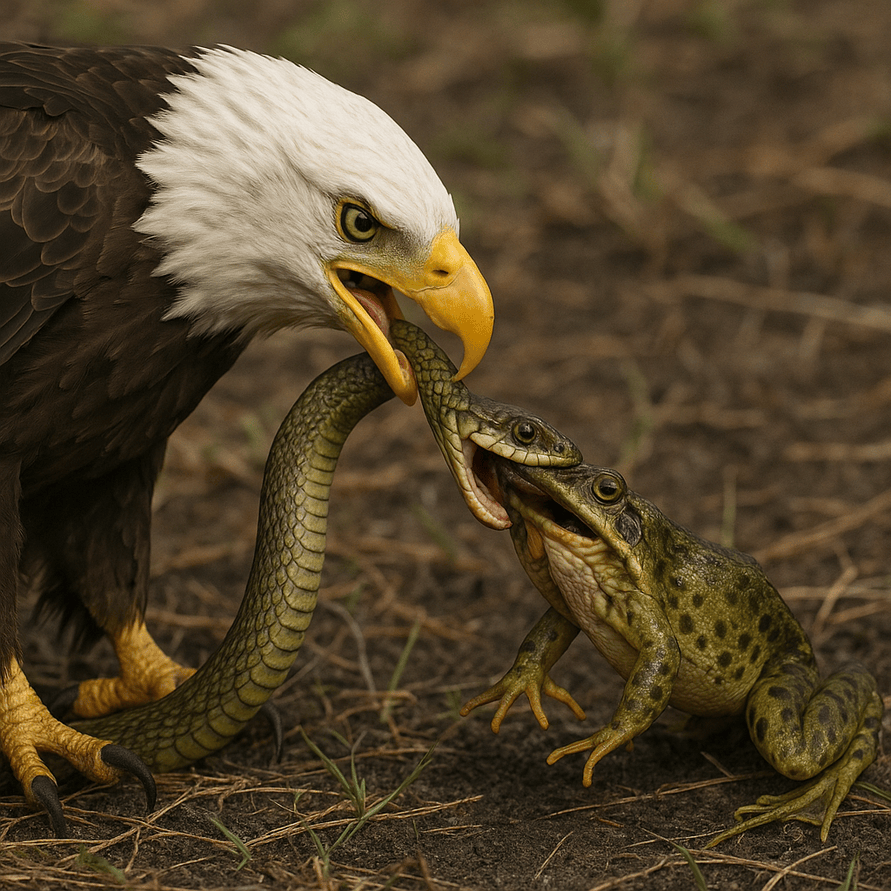
Ecology: Food Chain
What is a Food Chain? Transfer of food energy from green plants (producers) through a series of organisms with repeated eating and being eaten link is called a food chain. E.g. Grasses → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk/Eagle. … Continue reading
Ecology: Concepts
Ecocline Ecocline is a zone of gradual but continuous change from one ecosystem to another when there is no sharp boundary between the two in terms of species composition. Ecocline occurs across the environmental gradient (gradual change in abiotic factors … Continue reading
Ecology: Ecotones
What is it? An ecotone is a transitional area between two distinct ecological communities or ecosystems, where different habitats meet and integrate. These areas exhibit characteristics of both adjoining ecosystems and often contain unique species not found in the overlapping … Continue reading
Ecology: Habitats
What is it? Habitats are natural environments where specific plants, animals, and other organisms live. They provide the necessary conditions for survival, growth, and reproduction of these organisms. Types of Habitats Terrestrial Habitats: These are land-based habitats like forests, grasslands, … Continue reading
Ecology: Decomposers Or Saprotrophs Or Osmotrophs
Decomposers This refers specifically to organisms that break down dead organic matter (plants, animals, etc.) into simpler inorganic compounds. They play a vital role in recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem for producers (plants) to use. Examples include bacteria, fungi, … Continue reading
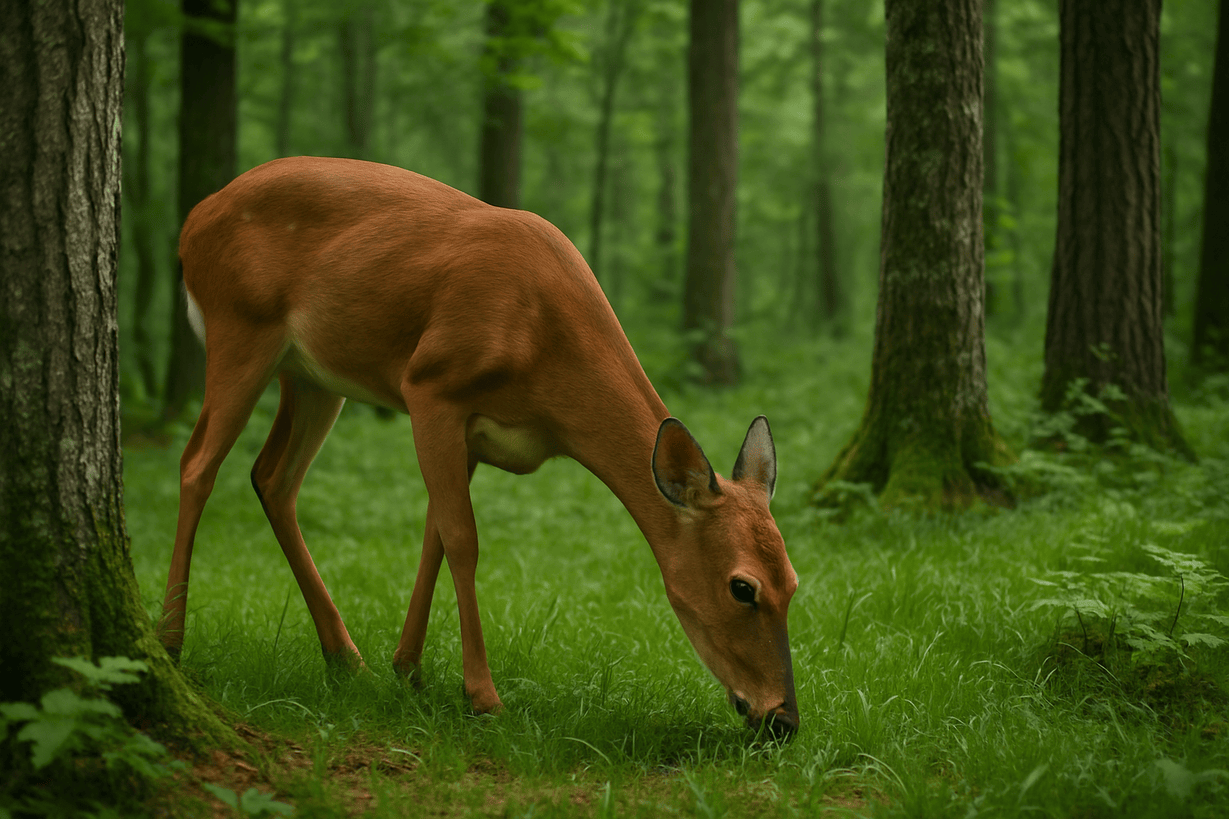
Ecology: Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Consumers
Primary Consumers (Herbivores) These are plant-eating organisms. They occupy the second level of a food chain, directly consuming producers. Examples: Cows, deer, rabbits, insects that eat leaves. Secondary Consumers (Carnivores) These are meat-eating organisms. They occupy the third level of … Continue reading
Ecology: Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
Autotrophs What is it?: Autotrophs are organisms that can produce their own food using sunlight, water, carbon dioxide, and other chemicals. Since they can produce their food they are also known as primary producers. Origin of Term: The word autotrophs … Continue reading