General Studies 3
Ecology: Oxygen Cycle (Gaseous Cycle)
What is it? The transfer of oxygen through the atmosphere (air), Biosphere (plants and animals), and Lithosphere (the earth’s crust) is referred to as the oxygen cycle. The oxygen cycle depicts how free oxygen is produced and used in each … Continue reading
Ecology: Nitrogen Cycle (Gaseous Cycle)
What is it? The nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates through the atmosphere, and the terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through … Continue reading
Ecology: Biotic Interaction
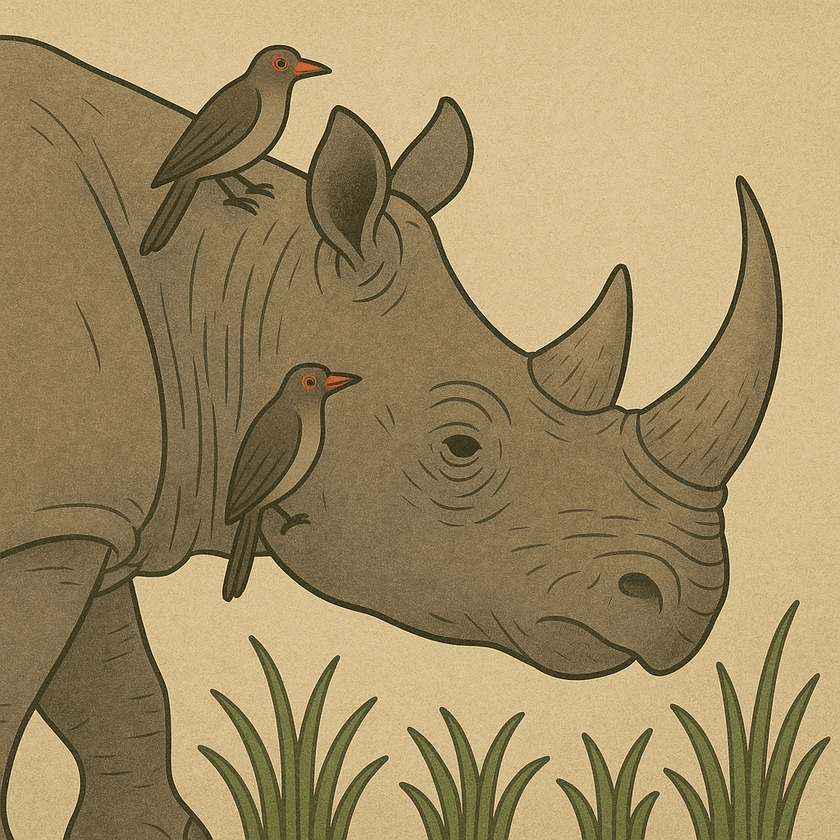
Mutualism It is a mutually beneficial relationship between two organisms. For example – Rhinos and Oxpeckers Commensalism In this interaction one species is benefited and other one is neither benefited or harmed. For example – Shark and sucker fish. Parasitism … Continue reading
Ecology: Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification
Bioaccumulation Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. It occurs when an organism absorbs a substance at a rate faster than that at which the substance is lost or eliminated by … Continue reading
Ecology: Ecological Efficiency
Ecological efficiency describes the efficiency with which energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next. The number of trophic levels in the grazing food chain is restricted as the transfer of energy follows 10 percent law – only … Continue reading
Ecology: Ecological Pyramids
What is an Ecological Pyramid? Ecological Pyramid is a graphical depiction which is meant to illustrate the relationship between different living organisms at different trophic levels in an ecosystem Each of the bars that make up the pyramid represents a … Continue reading
Ecology: Food Web
Multiple interlinked food chains make a food web. Food web represents all the possible paths of energy flow in an ecosystem. The food web provides more than one alternative for food to most of the organisms in an ecosystem and … Continue reading
Ecology: Food Chain
What is a Food Chain? Transfer of food energy from green plants (producers) through a series of organisms with repeated eating and being eaten link is called a food chain. E.g. Grasses → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk/Eagle. … Continue reading
Ecology: Concepts
Ecocline Ecocline is a zone of gradual but continuous change from one ecosystem to another when there is no sharp boundary between the two in terms of species composition. Ecocline occurs across the environmental gradient (gradual change in abiotic factors … Continue reading
Ecology: Ecotones
What is it? An ecotone is a transitional area between two distinct ecological communities or ecosystems, where different habitats meet and integrate. These areas exhibit characteristics of both adjoining ecosystems and often contain unique species not found in the overlapping … Continue reading