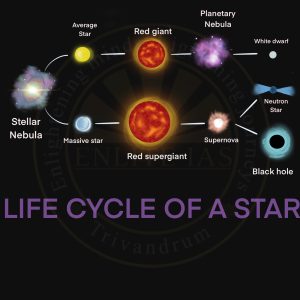
Life Cycle of Star
Associated Terms
- Nebula
- A cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and dust in space. Nebulae are the birthplaces of stars.
- T Tauri Star
- A young star still undergoing gravitational contraction.
- It represents an intermediate stage between a Protostar & a low-mass main sequence star.
- Protostar
- A Protostar looks like a star, but its core is not yet hot enough for nuclear fusion.
- Protostars are usually surrounded by dust, which blocks the light that they emit, so they are difficult to observe in the visible spectrum.
- Red Dwarf
- The faintest main sequence stars are called the red dwarfs.
- Because of their low luminosity, they are not visible to the naked eye.
- Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to the Sun, is a red dwarf.
- Red Giant
- A red giant is a stage in the evolution of a star that has exhausted the hydrogen fuel in its core.
- As the core contracts and heats up, the outer layers of the star expand and cool, causing the star to increase in size and become much brighter.
- During the red giant stage, the star fuses helium into heavier elements in a shell around the core.
- This shell fusion generates more energy than the fusion reactions in the core, causing the outer layers of the star to expand and cool.
- Red Supergiant
- A red giant star is a large, ageing star that has expanded and cooled down, causing it to appear red in colour.
- It occurs in the later stages of a star’s life cycle when it exhausts its hydrogen fuel and starts burning heavier elements.
- Planetary Nebula
- Planetary nebula is an outer layer of gas and dust that is lost when the star changes from a red giant to a white dwarf.
- White Dwarf
- A white dwarf is a very small, hot star, whose nuclear energy supplies have been used up.
- It consists of degenerate matter with a very high density due to gravitational effects, i.e., one spoonful has a mass of several tonnes.
- It is the last stage in the life cycle of a star like the Sun.
- Black Dwarf
- A black dwarf is a white dwarf that has sufficiently cooled and no longer emits significant heat or light.
- Supernova
- A supernova is the explosive death of a star and often results in the star obtaining the brightness of 100 million suns for a short time.
- A great proportion of primary cosmic rays comes from supernovae.
- Neutron Stars
- Neutron stars are composed mainly of neutrons and are produced after a supernova, forcing the protons and electrons to combine to produce a neutron star.
- A neutron star is very dense.
- Black Holes
- Black holes are believed to form from massive stars at the end of their lifetimes.
- The density of matter in a black hole cannot be measured.
- The gravitational pull is so great that nothing can escape from it, not even light.
