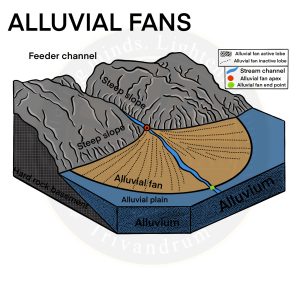
Alluvial Fans
- An alluvial fan is a cone-shaped depositional landform built up by streams, heavy with sediment load.
- Alluvial fans are formed when streams flowing from mountains break into foot slope plains of low gradient.
- Normally a very coarse load is carried by streams flowing over mountain slopes. This load gets dumped as it becomes too heavy to be carried over gentler gradients by the streams
- Furthermore, this load spreads as a broad low to a high cone-shaped deposit called an alluvial fan that appears as a series of continuous fans.
Floodplains
- Deposition develops a floodplain just as erosion makes valleys.
- Rivers in the lower course carry large quantities of sediments
- Large sized materials are deposited first when stream channel breaks into a gentle slope.
- Sand, silt and clay and other fine sized sediments are carried over gentler channels by relatively slow-moving waters.
- During annual or sporadic floods, these materials are spread over the low lying adjacent areas. A layer of sediments is thus deposited during each flood, gradually building up a floodplain.
- In plains, channels shift laterally and change their courses occasionally leaving cut-off courses which get filled up gradually by relatively coarse deposits.
- The flood deposits of spilt waters carry relatively finer materials like silt and clay.

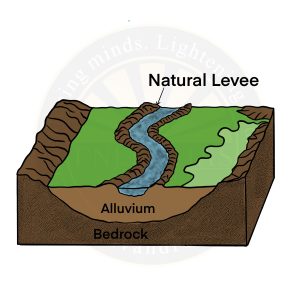
Natural Levees
- They are found along the banks of large rivers.
- They are low, linear and parallel ridges of coarse deposits along the banks of rivers on both sides due to deposition action of the stream, appearing as natural embankments.
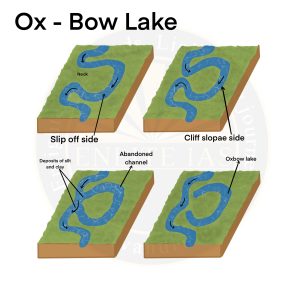
Oxbow Lakes
- In the lower course of rivers, meanders become very much more pronounced.
- As meanders grow into deep loops, they may get cut-off due to erosion at the inflexion points and are left as independent water bodies, known as ox-bow lakes.
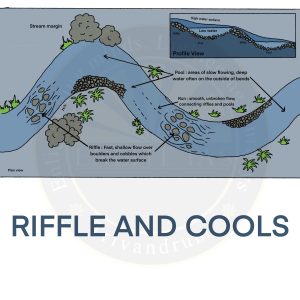
Riffles and Pools
- Pools: An area of the stream characterized by deep depths and slow current. Pools are typically created by the vertical force of water falling down over logs or boulders.
- Riffles: An area of stream characterized by shallow depths with fast, turbulent water. The riffles are short segments of the stream where water flow is agitated by rocks.
Bluff
- A bluff is a small, rounded cliff that usually overlooks a body of water, or where a body of water once stood.
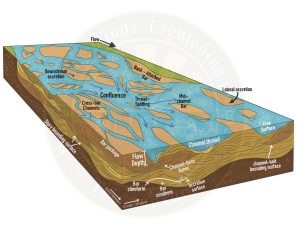
Braided Channels
- A braided channel consists of a network of river channels divided into multiple threads and separated by small and often temporary islands called eyots.
- Braided channels are commonly found where water velocity is low and the river is heavy with sediment load.
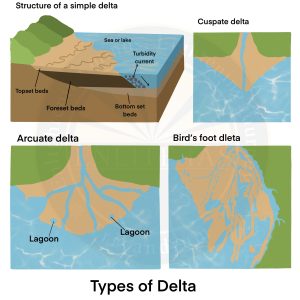
Delta
- The depositional feature of almost triangular shape at the mouth of a river debouching either in lake or a sea is called delta.
- For example – Ganga Delta
- Conditions for formation of delta
- Active vertical and lateral erosion in the upper course of the river to provide extensive sediments to be eventually deposited as deltas.
- The coast should be sheltered and preferably tideless.
- The sea adjoining the delta should be shallow or else the load will disappear in the deep waters.
- There should be no large lakes in the river to filter off the sediments.
- There should be no strong current running at right angles to the river mouth, washing away the sediments.
- Types of delta