Definition
- A fold is an undulating structure (wave-like) that forms when rocks or a part of the earth’s crust is folded (deformed by bending) under compressional stress. The folds are made up of multiple strata (rock layers).
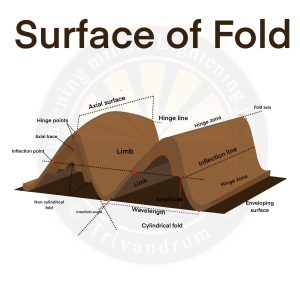
Parts of Fold
- Hinge Line: The line connecting points of maximum curvature in a fold.
- Axial Plane: A plane that divides the fold into two symmetrical halves.
- Limbs: The two sides of a fold, which may dip at varying angles.
- Crest: The highest point of an anticline.
- Trough: The lowest point of a syncline.
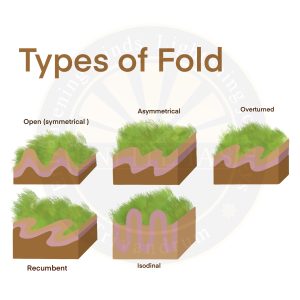
Types of Fold
- Symmetrical Fold: A symmetrical fold is one in which the axial plane is vertical.
- Asymmetrical Fold: An asymmetrical fold is one in which the axial plane is inclined.
- Isoclinal Fold: An isoclinal fold has limbs that are essentially parallel to each other and thus approximately parallel to the axial plane.
- Overturned Fold: An overturned fold has a highly inclined axial plane such that the strata on one limb are overturned.
- Recumbent Fold: A recumbent fold has an essentially horizontal axial plane.