Money and Money Supply
Barter System
- Definition- The Barter System refers to the act of trading goods and services between two or more parties directly, without the use of an intermediary monetary medium, such as money or credit card.
Money
- Definition – Money is defined as something that is generally accepted by society as a medium of exchange and which can act as a unit of account, a store of value, and be used for repayment of debt.
- Major Functions of Money –
- Medium of Exchange: Facilitating transactions by providing a universally accepted means of payment.
- Unit of Account: Providing a common measure of value for goods and services, simplifying economic calculations.
- Store of Value: Allowing individuals to hold wealth in a stable and easily accessible form for future use.
- Standard of Deferred Payment: Enabling contracts and debt settlements denominated in money, facilitating credit transactions.
Types of Money
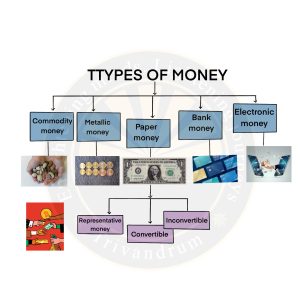
- Commodity money: Commodity money refers to a type of currency that derives its value from the intrinsic worth of the commodity it is made of. For example – gold, silver, copper.
- Metallic Money: Metallic Money refers to money that is made up of pure and superior metals like gold and silver. Convenience, storability, high-value density, and easy portability led metallic money to take the place of commodity money.
- Paper Money: Paper money consists of currency notes issued by the government or the central bank of a country.
- Fiat Money: Fiat money is a type of currency that is not backed by a physical commodity, such as gold or silver. Its value is derived from the government that issues it and the public’s faith in that government. Currency notes and coins in India are examples of fiat money.
- Plastic Money: Plastic money is a term that is used predominantly in reference to the hard plastic cards in place of actual bank notes. They can come in many different forms such as cash cards, credit cards, debit cards, etc.
- Helicopter Money or Helicopter Drop: Helicopter Money or Helicopter Drop refers to increasing the supply of money in an economy through measures such as more spending, tax cuts, etc.
- Near Money: Near money denotes assets that, while not classified as currency, possess the inherent capability for swift and seamless conversion into cash without significant loss of value.
- Hard Money: Money with backing of gold or other credible assets. It avoids the risk of inflation.
- Soft Money: A soft currency is one with a value that fluctuates, predominantly lower relative to other currencies, because there is less demand for that currency in the forex markets.
- Hot Money: Hot money’ refers to funds controlled by investors seeking short-term returns. It is the flow of funds from one country to another to earn a short-term profit on interest rate differences.

