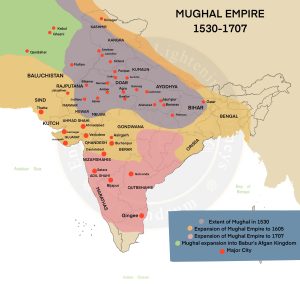
Mughal Empire: 1526 – 1857 CE
- Babur founded the Mughal empire in 1526, after defeating Ibrahim Lodi in the first battle of Panipat.
- The “Great Mughals” dynasty, consisting of Babur, Humayun, Akbar, Jahangir, Shah Jahan, and Aurangzeb, made significant contributions to Indian history.
- The empire fell following Aurangzeb’s death in 1707 due to coming weak rulers.
Babur (1526-1530 CE)
- Babur (Zahiruddin Muhammad) was a descendant of Turco-Mongol conqueror Timur on his father’s side and Genghis Khan on his mother’s.
- In the 15th century, the Timurids ruled much of Central Asia before being driven away by the increasing Safavid authority.
- Babur rose to the throne of a minor Fergana kingdom at the age of twelve, but he quickly lost control of his family domain.
- Babur took control of Kabul at the age of 24 in 1504 and then reached India via the Khyber Pass.
- He defeated Ibrahim Lodi of the Lodi dynasty in the 1st battle of Panipat in 1526 and established the Mughal Dynasty in India.
First Battle of Panipat (1526)
|
Other Battles
- Battle of Khanwa 1527– Babur and Rana Sanga’s armies met at Khanwa, near Fatehpur Sikri. Rana Sanga faced defeat in 1527, and Babur’s superior military tactics once again proved successful. The fall of Rana broke the strongest challenge in north India.
- The Battle of Chanderi, 1528- Babur defeated Medini Rai at Chanderi.
- Battle of Ghagra in 1529– Babur fought Afghans (Ibrahim Lodi’s brother Mohammad Lodi) and destroyed them.
Contributions
- He was a scholar of Persian and Arabic.
- He penned his autobiography, Tuzuk-i-Baburi, in the Turki language. Later, it was translated into Persian, among other languages.
Humayun (1530-40 & 1555-56)
- He had to deal with the fast rise in power of the Afghans and the Bahadur Shah of Gujarat.
- In the Battle of Chausa in 1539, Sher Khan (Sher Shah Suri) defeated Humayun near Buxar. He had to flee from the combat.
- In the Battle of Kannauj in 1540, Sher Khan defeated Humayun again. He fled again and remained in exile for fifteen years.
- He sought refuge at the Iranian king’s court and, with his support, conquered Kandahar and Kabul in 1545.
- Humayun conquered Delhi in 1555, following the collapse of the Suri Empire, but died the next year.
- Humayun established a new city in Delhi that he named “Dinpanah”.
- He built mosques in Delhi including the Jamali mosque and the Isa Khan mosque.
- His wife, Amida Benu Begum, built Humayun’s tomb (UNESCO site).
- Humayun’s sister, Gul Badan Begum, wrote “Humayun-Nama” in the Persian language.
- Humayun patronized the Mughal painting during his time in Persia.
Sur Dynasty – Sher Shah Sur (1540-45 CE)
|
