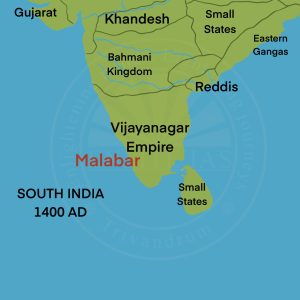
Bahmani Empire: (1347-1527 CE)
- The Bahmani Kingdom was founded by Hasan Gangu Bahmani.
- He established an independent Muslim state of Deccan in India’s southern provinces.
- The Bahmani Kingdom began to expand following the triumph of the insurrection against Muhammad-Bin-Tughlaq in 1327 CE.
Important Rulers
Muhammad Shah-I (1358-1375 CE)
- He defeated Bukka-I of Vijayanagar, and Kapila Nayaks of Warangal.
Muhammad Shah-ll (1378-1397 CE)
- He was a peaceful ruler who established positive relationships with his neighbors.
- He erected numerous mosques, madrasas (places of learning), and hospitals.
Feroz Shah Bahmani (1397-1422 CE)
- Taj ud-Din Feroz Shah was regarded as the greatest Sultan of the Bahmani Kingdom.
- He defeated the Vijayanagara Empire’s Emperor Deva Raya I and married his daughter.
- He established the city of Firozabad on the banks of the Bhima River.
- He was an admirer of art, poetry, and culture.
Ahmad Shah (1422-1435 CE)
- Conquered Warangal.
- Shifted capital from Gulbarga to Bidar.
Muhammad Shah III (1463-1482 CE)
- Became Sultan at the age of nine due to this Muhammad Gawan became the regent.
- Muhammad Gawan
- Gawan made the kingdom very powerful by defeating the rulers of Orissa, Konkan, Sangameshwar, and Vijayanagar.
- Gawan was able to eliminate corruption to a good extent.
- Bahmani court nobles were envious of Gawan. They plotted against him and were successful in convincing the Sultan of Gawan’s treason. He was executed in 1482 CE, and his death affected the strength of the Bahmani Kingdom.
- The kingdom was succeeded by weak rulers.
- Later resulting in its disintegration.
Kingdoms Formed from the Bahmani Kingdom
The Adil Shahis of Bijapur (1490-1686 CE)
- Yusuf Adil Shah created the state of Bijapur in 1489 CE
- Ibrahim (1534-58) was the first Bijapur ruler who replaced Persian with Hindvi (Dakhini Urdu) as the official language.
- Muhammad Adil Shah built Gol Gumbaz.
- Ibrahim II (1580-1627) was lovingly known as Jagadguru among his subjects. Aurangzeb annexed Bijapur in 1686.
The Nizam Shahis of Ahmednagar (1490-1633 CE)
- Founded by Ahmad Bahri in 1490.
- Chand Bibi defended the kingdom against the Mughals
- Shahjahan conquered Ahmedabad in 1636 CE.
The Qutub Shahis of Golconda (1518-1687 CE)
- Founded by Ali Qutub Shah in 1518.
- Muhammad Quli founded the city of Hyderabad.
- Aurangzeb annexed Golconda in 1687.
The Imadshahis of Berar (1490-1574 CE)
- Founded by Fatullah Imad-ul-Mulk in 1490 CE
- It was annexed by Nizam Shahis in 1572 CE
The Barid Shahis of Bidar (1528-1619 CE)
- Founded by Ali Barid in 1518.
- Adil Shahis annexed the kingdom
- It was also annexed by Aurangzeb in 1657.
Administration
- The Bahamians appear to have adopted the administrative structure of the Delhi Sultanate.
- The Bahmani kingdom was divided into Tarafs, which were initially four in number. Each taraf was led by a tarafdar. During Mahmud Gawan’s rule, the Empire expanded and the realm was divided into eight tarafs.
- The nobility was divided into two groups: Afaqis or Pardesis (foreigners) and Deccanis (locals). Both sides were in continual dispute.
- The army commander’s name was Amir-Ul-Umara. The sultans also possessed a considerable contingent of bodyguards known as khassakhel.
Society
- The social nature was cosmopolitan, with people of diverse nationalities, including Hindus, Muslims, Iranians, and Abyssinians, living in the Bahmani kingdoms.
- Languages were widely spoken throughout the kingdom, including Dakhani (proto-Urdu), Marathi, Kannada, and Telugu.
- Ibrahim Adil Shah used Dakhini instead of Persian, as Nikitin, a Russian explorer, described two classes: the wealthy nobility and the destitute general populace.
- The Bahamian ruler held Sufis in high regard.
- The Bahamani kingdom had a Shia impact due to a large influx of Afaqis (foreign, usually Iranian nobles).
Literature
- The literary works in Persian, Arabic, and Urdu flourished during this time.
- Mohammad Gawan wrote poetry in Persian, including Riyaz-ul-Insha and Manazir-ul-Insha.
- During this period, a new dialect known as “Dakhini urdu” gained popularity.
- Khwaja Bande Nawaz Gesu Daraj, a well-known sufi saint from Gulbarga, wrote Dakhini urdu
Art and Architecture
- High Persian influence includes – Tall minarets, Strong arches, Huge domes, Spacious Hazaras, and Crescent moon at the top of the building.
- Eg – Gol gumbaz, Charminar at Hyderabad, Jama Masjid at Gulbarga, the fort of Golconda and the tomb of Ahmad Shah at Bidar.
