- Composition: Primarily methane, with varying amounts of higher alkanes, and small percentages of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, or helium.
- Types of Gases
- Associated Gas: Natural gas found with oil (wet gas).
- Non-Associated Gas: Gas found without oil (dry gas).
- Sour Gas: Gas containing hydrogen sulfide or other sulfur compounds.
- Sweet Gas: Coalbed methane without hydrogen sulfide.
- Calorific Value: Natural gas is typically bought and sold based on its energy content, often measured in MMBTUs (millions of British thermal units).
- Odorization: Natural gas is odorless, but a safety compound (mercaptan) is added to give it a distinctive smell.
- Formation of Natural Gas: Formed over millions of years when decomposing plant and animal matter is exposed to heat and pressure beneath the Earth’s surface, trapping energy in chemical bonds.
- Uses of Natural Gas
- Domestic: Used for cooking, heating, and powering appliances.
- Compressed Natural Gas (CNG): Used for transportation, offering a cleaner alternative for low-load vehicles.
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG): Powers vehicles such as off-road trucks and trains.
- Industrial: Used in power generation, rubber compounding, and chemical production (e.g., ammonia for fertilizers).
- Renewable Energy Support: Powers turbines for wind and solar energy production.
- Importance of Natural Gas to India
- Primary Consumption: About 40% is used for fertilizer production, 30% for power generation, and 10% for LPG.
- Power Sector: Gas-fired power stations provide about 10% of India’s electricity but often operate below capacity due to a shortage of feedstock.
- Energy Mix: Natural gas accounts for about 6% of India’s energy consumption, much lower than coal and crude oil. The government aims to increase this share to 15% by 2030.
- Energy Security: India faces challenges due to insufficient oil reserves and reliance on expensive imported LNG.
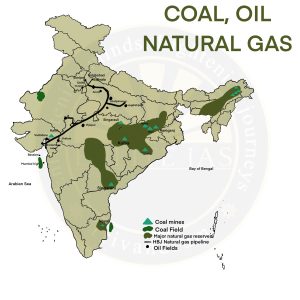
- Distribution of Natural Gas in India
- Major fields: Assam, Gujarat, Bombay High, KG Basin, Tripura, Odisha, Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Reserves
- 541 BCM (onshore) in Assam and Gujarat.
- 190 BCM offshore in the Bay of Cambay and Bombay High.
- 400 BCM in the Tripura Basin.
- 1700 BCM estimated in Andaman and Nicobar Islands (economic viability yet to be established).