Why in the news?
- Union Science and Technology Minister said the ministry is working on stem cell therapy and genetic solutions for diabetes, while expressing concern over the cases in India.
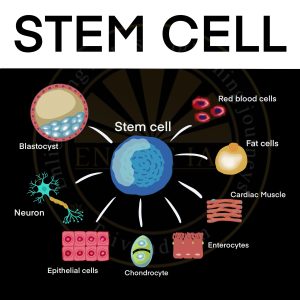
Stem Cells
- The smallest functional unit of life is called the Cell.
- Bone marrow, Umbilical cord blood, Adipose tissue, Allografts, Amniotic fluid etc are the source of stem cells.
Stem Cell Therapy
- Types
- Regenerative therapy: Using stem cells to regenerate damaged tissues or organs.
- Transplantation: Replacing damaged or diseased stem cells (e.g., in bone marrow transplants).
- Autologous stem cell therapy: Using the patient’s own stem cells.
- Allogeneic stem cell therapy: Using donor stem cells.
- Applications of Stem Cell Therapy:
- Blood and immune system disorders: Conditions like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma can be treated through stem cell transplants.
- Bone and cartilage repair: Stem cells are used to heal damaged bones or regenerate cartilage, especially in cases of severe injury or arthritis.
- Neurological conditions: Emerging therapies focus on repairing neurons in conditions like Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and spinal cord injuries.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Experimental treatments aim to regenerate heart tissue after heart attacks or in chronic heart diseases.
- Diabetes: Research is ongoing to use stem cells to generate insulin-producing cells for the treatment of Type 1 diabetes.
- Eye disorders: Stem cell therapy is being studied to restore vision in patients with retinal diseases.
- Skin regeneration: Burn victims or patients with skin diseases benefit from stem cell-based skin regeneration treatments.
- Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy:
- Personalized treatment: Autologous stem cell therapy reduces the risk of immune rejection.
- Repair and regeneration: Stem cells can aid in the repair of tissues and organs that do not naturally regenerate well.
- Challenges and Ethical Concerns
- Ethical concerns: Particularly with the use of embryonic stem cells, as it involves the destruction of embryos.
- Immune rejection: In allogeneic therapies, the patient’s immune system may reject donor stem cells.
- Tumor formation: There is a risk that transplanted stem cells might form tumors (teratomas) if not properly controlled.
- High cost: Stem cell treatments can be expensive and are not always covered by insurance.
