Taxation
- Taxation is a term for when an authority, mostly a government, imposes a financial obligation on its citizens/ residents/corporations/companies etc.
- It is a way of Income redistribution.
Associated Terms
- Tax Incidence: It is the one who actually pays tax. The true burden of a tax is given by incidence and not impact.
- Tax Impact: It is the entity on whom tax is imposed. The entity has the legal responsibility to pay taxes.
- Tax Shifting: When a tax’s incidence differs from the tax’s impact.
- Tax base: Volume of goods and services on which tax is imposed.
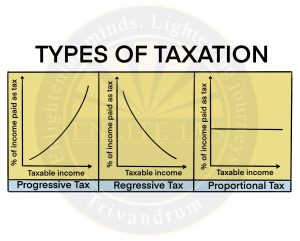
Types of Taxation
- Progressive Taxation
- Based on the taxpayer’s ability to pay.
- High income earners will pay more tax than low-income earners.
- Example – Income Tax
- Regressive Taxation
- A regressive tax is a tax applied uniformly, taking a larger Percentage of income from low-income earners than from high-income earners.
- It is in opposition to a progressive tax, which takes a larger percentage from high-income earners.
- Proportional Taxation
- The same percentage tax is levied on everyone regardless of income.
- Retrospective Taxation
- It allows a country to pass a rule on taxing certain products, items or services and deals and charge companies from time before the date on which the law is passed.
- Countries use this route to correct any anomalies in their taxation policies that have, in the past, allowed companies to take advantage of such loopholes.