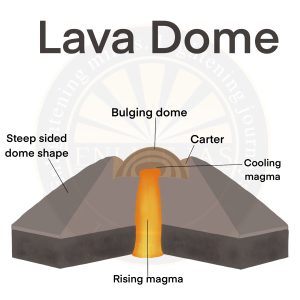
Cinder Cones
- Cinder cones are circular or oval cones made up of small fragments of lava from a single vent that have been blown up.
- Cinder cones result from eruptions of mostly small pieces of scoria and pyroclastics that build up around the vent.
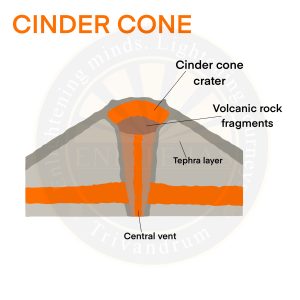
Composite Volcano
- Composite volcanoes are steep-sided volcanoes composed of many layers of volcanic rocks, usually made from high-viscosity lava, ash and rock debris.
- These types of volcanoes are tall conical mountains composed of lava flows and other ejecta in alternate layers or strata, that gives it its name.

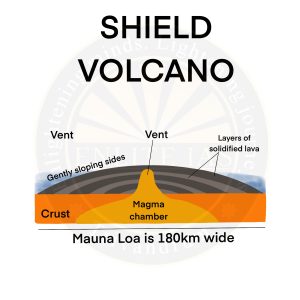
Shield Volcano
- Shield volcanoes are volcanoes shaped like a bowl or shield in the middle with long gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows.
- These are formed by the eruption of low-viscosity lava that can flow a great distance from a vent.
- They generally do not explode catastrophically.
- For example – Hawaiian volcanoes
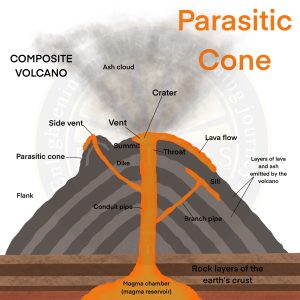
Parasitic Cones
- These are formed in the vicinity of the main cone and feed on the main cone.
- For example – Shasta volcano, USA
Lava Domes
- Lava domes are formed when erupting lava is too thick to flow and makes a steep-sided mound as the lava piles up near the volcanic vent.
- They are built by slow eruptions of highly viscous lava.