
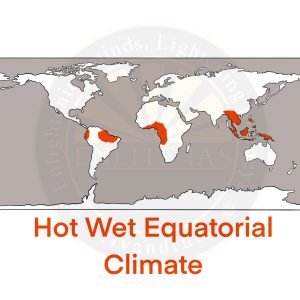
Hot, Wet Equatorial Climate
- Distribution
- 50o North – 100o South from the equator.
- It is found in the Amazon basin, Congo basin, and South – East Asia.
- Climate
- There is great uniformity of temperature throughout the year.
- The mean monthly temperature is between 24o to 27ºC.
- There is no winter.
- The diurnal and annual range of temperature is small.
- Precipitation is heavy and well-distributed throughout the year.
- Natural Vegetation
- It supports a luxuriant type of vegetation with heavy undergrowth which include epiphytic and parasitic plants.
- The Amazon tropical rain forest is known as Selvas.
- Trees of a single species are very scarce in such vegetation.
- Major species are mahogany, and ebony.
- Wildlife
- Different types of monkeys and apes.
- Economy
- The equatorial regions are generally sparsely populated.
- Primitive people are mainly engaged in shifting cultivation.
- Plantation agriculture like natural rubber, cocoa and others are also practised.
| Name of Shifting Cultivation | Region |
| Ray | Vietnam |
| Tavi | Madagascar |
| Masole | Congo (Zaire river Valley) |
| Fang | Equatorial African Countries |
| Logan | Western Africa |
| Comile | Mexico |
| Milpa | Yucatan and Guatemala |
| Echalin | Guadeloupe |
| Milya | Mexico and Central America |
| Konuko | Venezuela |
| Roka | Brazil |
| Chetemini | Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe |
| Caingin | Philippines |
| Taungya | Myanmar |
| Chena | Sri Lanka |
| Ladang | Java and Indonesia |
| Tamrai | Thailand |
| Humah | Java and Indonesia |
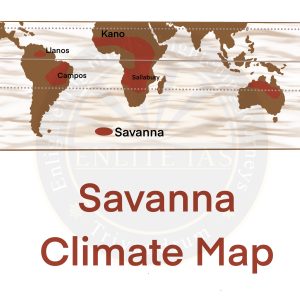
Savanna or Sudan Climate
- What is it?: Savanna or Sudan climate is a transitional type of climate found between the equatorial forests and trade wind hot deserts.
- Distribution
- It is located between 5o – 20o latitudes on either side of the equator.
- It is best developed in Sudan where the dry and wet seasons are most distinct, hence the name – Sudan Climate.
- The belt includes West African Sudan, and then curves southwards into East Africa and southern Africa, north of the Tropic of Capricorn.
- In South America, there are two distinct regions of savannah located north and south of the equator, namely the llanos of the Orinoco basin and the Campos of the Brazilian Highlands.
- Climate
- Temperatures range between 20 to 32 degrees centigrade for lowlands, but the range increases as one moves away from the equator.
- Annual average temperature is around 18 degrees centigrade.
- The region has alternative wet and dry seasons.
- Vegetation
- Tall grass and little trees make up much of the local vegetation. ‘Parkland’ or ‘bush-veld’ are other terms for grassland.
- The trees are of the deciduous variety.
- Major tree species are Acacia, baobabs, and bottle trees.
- Wildlife
- Herbivores – zebra, giraffe, elephant, antelope etc.
- Carnivores – lion, hyena, leopard.
- Economy
- The region has nomadic pastoralists such as the Masai, who are found in Kenya and Tanzania of Africa. They are dependent on their animal stock for their survival and lead a primitive lifestyle.
- Settled agriculture is also practised by many tribes such as the Hausa, who have also domesticated animals for their use in crop cultivation.
- Plantation crops like cotton, sugarcane, oil palm, groundnuts, coffee, and tropical fruits are cultivated.
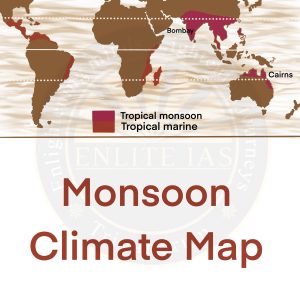
Tropical Monsoon Climate
- What is it?
- Monsoon climate, also known as the tropical monsoon climate, is found in the region bounded by the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- The region is influenced by the movement of the inter-tropical convergence zone (ITCZ) and is hot and humid all around the year because the sun remains overhead.
- Distribution
- They are confined within 5o – 30o latitudes on either side of the equator.
- Indian subcontinent, Indo-China (Laos. Vietnam, Cambodia), Thailand, southern China and northern Australia are the regions experiencing this climate.
- Climate
- Average monthly temperature is above 18 degrees centigrade, but in summers the maximum can reach as high as 45 degrees centigrade.
- Annual average rainfall is around 200-250 cm.
- Natural Vegetation
- They can be of two types: moist deciduous, where the rainfall exceeds 150 cm, and dry deciduous, where the average annual rainfall is less than 150 cm.
- Major tree species are sal, teak, neem, and shisham.
- Wildlife
- Some common monsoon forest animals are monkeys, large cats, parrots, rodents, ground-dwelling birds, and reptiles.
- Economy
- Major economic activity is agriculture and major crops are
- In the plains of north India, cereals like rice, wheat, maize etc. are cultivated apart from jute, sugarcane, and spices.
- In the highlands of south and east India, plantation crops can be found – tea, coffee, rubber, banana etc
- Major economic activity is agriculture and major crops are
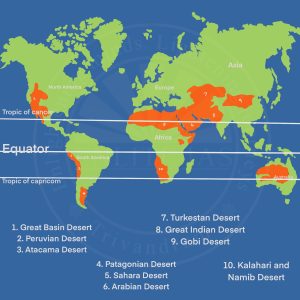
Desert Climate
- Hot Deserts
- Distribution
- Important hot deserts of the world are situated on the western edges of the continents between latitudes 15o to 30o north and south.
- Major Hot Deserts – Great Australian Desert, Arabian desert, Kalahari desert, Thar desert, Mohave, Sonoran, Californian, and Mexican deserts.
- Climate
- The average summer temperatures are always above 30 degrees centigrade.
- The hottest temperature to be recorded was in Libya in 1922. The temperatures rose as high as 57 degrees centigrade.
- Cloudless skies, intense insolation, dry air, and a rapid rate of evaporation are the reasons for such high temperatures.
- The diurnal temperature range is very high.
- Average annual precipitation in these regions is not more than 25 cm.
- Distribution
- Mid-Latitude Deserts
- Distribution
- They include the Gobi Desert, the Turkestan Desert, the Patagonian Desert etc.
- Climate
- The climatic conditions of these deserts are similar to those of the hot deserts.
- Average annual precipitation does not exceed 25 cm.
- Distribution
- Common Features of Hot Deserts and Mid-Latitude Deserts
- Vegetation
- The region has saline soil.
- The region has thorny vegetation like cactus, grass, scrubs, weeds, etc
- Adaption of Plants
- Common adaptations include water storage in stems and leaves, waxy coverings on leaves, shedding leaves, all to minimize water loss.
- Some have developed long taps roots to be able to reach water tables.
- Wildlife
- Common animals are foxes, desert eagles, and camels.
- Adaptation
- They are fast runners, long legs, concentrated urine, and have the ability to store water in their body.
- Economic Activity
- Nomadic herding, mining etc.
- Vegetation
Steppe Climate
- Other Name: The Steppe Climatic region is also known as Temperate Grasslands.
- Distribution
- Steppes are found in the continental interiors.
- They are usually found in the temperate latitudes and hence come under the influence of Westerly winds.
- Steppes are characterized by vast grasslands which are, by and large, devoid of trees.
- Local regions and names
| Local Names | Regions |
| Prairies | North America |
| Pustaz | Hungary |
| Pampas | Argentina and Uruguay |
| Velds | South Africa |
| Downs | Australia |
| Canterbury | New Zealand |
- Climate
- The average annual rainfall over the steppes varies from 25 to 75 cm.
- These regions are under the effect of continentality and hence experience extreme temperatures.
- Summers are warm with the average temperature in the range of 18-20 degrees centigrade.
- Winters are usually cold with occasional snowfall.
- They are known by various names such as Mistral (France), which is a cold dry wind; Loo (Gangetic plains), Sirocco (Sahara), Foehn (Alps) etc. are warm, dry winds.
- Vegetation: The region has treeless grasslands.
- Wildlife: Wolves, foxes, falcons, and eagles.
- Economy
- Livestock ranching
- The region is known as the wheat basket of the world.
Mediterranean Climate
- Distribution:
- The Mediterranean climate is found between 30o and 45o North and South of the Equator.
- It is found in the areas around the Mediterranean Sea, Central Chile, California, Cape Town in Africa, and Southern Australia.
- Climate: The Mediterranean climate is characterized by very distinctive climatic features with dry, warm summers and wet, cold winters, and local winds.
- Vegetation
- Trees have small, broad leaves and are widely spaced.
- The absence of shade is a peculiar feature of this climat,e and the growth is almost restricted to autumn and spring.
- Plants are in a continuous struggle against heat, dry air, excessive evaporation, and prolonged droughts.
- Tree species are oaks and pines.
- Economic Activity
- The region is important for fruit cultivation, cereal growing, wine-making and agricultural industries as well as engineering and mining.
- The region is a net exporter of citrus fruits and the net importer of dairy products.
China Type
- Distribution
- It is found along the eastern margins of the continents between 20o and 35o N and S latitude.
- Local Variety
- China Type: Temperate monsoon or China type is found in most parts of China and is a modified form of monsoonal climate.
- Gulf Type: It is found in the south-eastern parts of the USA bordering the Gulf of Mexico
- Natal Type: This climate is witnessed in New South Wales, Natal and Parana-Paraguay-Uruguay basin.
- Climate
- It is typified by a warm moist summer and a cool, dry winter.
- Rainfall is more than moderate and ranges between 60 cm to 150 cm and there is a uniform distribution of temperature throughout the year.
- Local storms also occur. Example: typhoons and hurricanes.
- Vegetation
- Due to heavier rainfall, the region supports luxurious vegetation.
- There is perennial plant growth and the conditions are well suited for a rich variety of plant life.
- The lowlands carry both evergreen broad-leaved forests and deciduous trees, similar to the tropical monsoon forests.
- In the highlands, there are various species of conifers such as pines and cypresses which are important softwoods.
- Economic Activity
- Cultivation of agriculture crops like paddy, cotton, and corn.
British Type Climate
- Distribution
- Northern Hemisphere – The climatic belt stretches from Britain into North-West Europe. It is also found in North America.
- Southern Hemisphere – The climate is experienced in southern Chile, Southern Australia, Tasmania and most parts of New Zealand, particularly in the South Island.
- Climate
- Moderately warm summers and fairly mild winters.
- Adequate rainfall throughout the year.
- British-type climatic regions are under the permanent influence of the Westerlies all round the year.
- The mean annual temperature is usually in the range of 5o C – 15o C.
- Vegetation
- The natural vegetation of this climatic type is the deciduous forest.
- The trees shed their leaves in the cold season.
- Some of the common species of temperate hardwood include oak, elm, ash, birch, beech, hornbeam, and poplar.
- Economic Activity
- Agriculture activities like mixed farming, market gardening, and sheep rearing.
- The countries are concerned in the production of machinery, chemicals and textiles.
- Industries are also based on dairy products in Denmark, Netherlands and New Zealand.
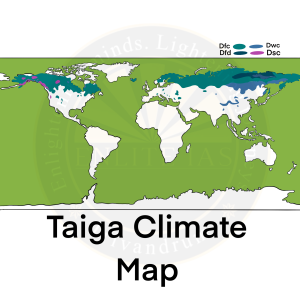
Taiga Climate
- Other Climate: Taiga Climate is also known as Cool Temperate Continental Climate and is popular by various other names such as Siberian Climate, and Boreal Climate.
- Distribution
- This type of climate is mainly found in the Northern Hemisphere in between 50o N to 70o N along a continuous belt across central Canada, some parts of Scandinavian Europe and most of central and southern Russian.
- Climate
- The climate of these regions is characterized by extremely cold winters of long duration, with temperatures ranging around – 30 C to – 40 C.
- The summers are cool and brief.
- Maritime influences are nearly absent in the interiors and hence the annual precipitation is low, generally around 38cm to 63 cm.
- Vegetation
- The predominant vegetation of this region is evergreen coniferous forests.
- Four major species of coniferous forests grow in the region: pine, fir, spruce, and larch.
- Economic Activity
- Trapping of animals and lumbering of trees.
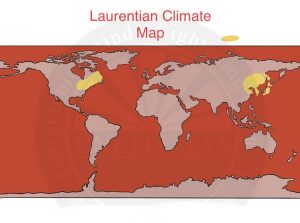
Laurentian Climate
- Other Name: Also called Cool Temperate Eastern Margin Climate.
- Distribution
- North American region – Eastern Canada, north-east USA, and Newfoundland.
- Asiatic region – The other region is the eastern coastlands of Asia, including North China, eastern Siberia, Manchuria, Korea and northern Japan.
- The climate is totally absent in the southern hemisphere.
- Climate
- The climate of this type has cold, dry winters and warm, wet summers.
- Two-thirds of the annual precipitation is in summer.
- Winters are dry and cold and westerlies blow out from the continental interiors.
- Vegetation:
- The predominant vegetation in this climate is cool temperate forests and they contain coniferous trees like pine.
- Economic Activity
- Lumbering and its associated timber, paper and pulp industries are the most important economic activities in the region.
Tundra Climate
- Distribution
- They have cold climatic conditions all through the year.
- They are found in Arctic and Antarctic circles.
- Climate
- Winters are long and very severe, summers are cool and brief.
- Precipitation is mainly in the form of snow, falling in winter and being drifted by the blizzards.
- Vegetation
- The region is occupied by mosses, lichens, and sedges.
- Economic Activity
- Eskimos live in Greenland, northern Canada, and Alaska and are involved in hunting, fishing, and food-gathering.


