Basics
- What is it?: The periodic rise and fall in the sea level is known as Tide.
- Caused due to
- The gravitational force exerted on Earth by the Sun.
- The gravitational force exerted on Earth by the Moon.
- Rotation of the Earth
- Tidal Range: The difference in height between the high tide and the low tide is called the tidal range.
Fact to Know
|
- Oscillating currents produced by tides are known as tidal streams.
- The moment that the tidal current ceases is called slack water or slack tide.
- Tides are commonly semi-diurnal (two high waters and two low waters each day), or diurnal (one tidal cycle per day).
Stages of Tides
- Sea level rises over several hours, covering the intertidal zone; flood tide.
- The water rises to its highest level, reaching high tide.
- Sea level falls over several hours, revealing the intertidal zone; ebb tide.
- The water stops falling, reaching low tide.
Types of Tides
- Based on Frequency
- Semi-Diurnal Tide
- An area has a semidiurnal tidal cycle if it experiences two high and two low tides of approximately equal size every lunar day.
- Semi-Diurnal Tide

-
- Diurnal Tide
- An area has a diurnal tidal cycle if it experiences one high and one low tide every lunar day.
- Diurnal Tide

-
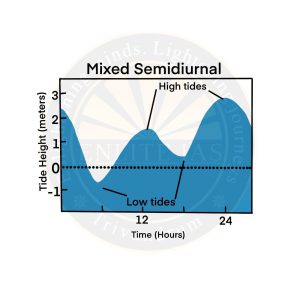
- Mixed Tide
- The mixed tidal cycle, or simply mixed tide, is formed by a tidal cycle with two unequal high and low tides.
- Mixed Tide
- Tides Based on the Sun, Moon and the Earth Positions
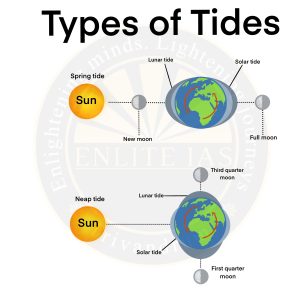
- Spring Tides
- Spring tides occur when Moon, Earth, and Sun fall in a straight line, which is called as syzygy (siz-eh-gee), the greatest difference between high and low tide water levels can be observed.
- These spring tides occur twice each month, during the full and new Moon.
- If the Moon is at perigee, the closest it approaches Earth in its orbit, the tides are especially high and low.
- Neap Tides
- When the Sun and Moon form a right angle, as when a half moon can be seen, their gravitational pulls fight each other and one can notice a smaller difference between high and low tides. These are called neap tides.
- Spring Tides
Significance of Tides
- Navigation
- Tidal heights are very important, especially in harbours near rivers and within estuaries having shallow ‘bars’ [Marine Landforms] at the entrance that prevent ships and boats from entering into the harbour.
- High tides help in navigation. They raise the water level close to the shores. This helps the ships to arrive at the harbour more easily.
- Tides generally help in making some of the rivers navigable for ocean-going vessels. London and Calcutta [Tidal Ports] have become important ports owing to the tidal nature of the mouths of the Thames and Hooghly respectively.
- Fishing
- The high tides also help in fishing. Many more fishes come closer to the shore during the high tide. This enables fishermen to get a plentiful catch.
- Desilting
- Tides are also helpful in desilting the sediments and in removing polluted water from river estuaries.

