Basics
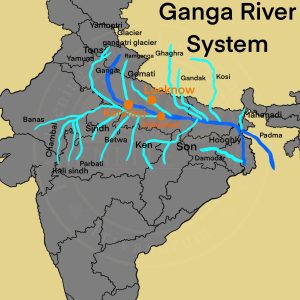
- Origin: The Bhagirathi, considered to be the source stream of Ganga rises at the foot of the Gangotri Glacier, at Gaumukh.
- Basin Countries: The Ganga river system is spread over India, Tibet, Nepal and Bangladesh.
- Fact: It is the largest river basin in India and accounts for one-fourth of the total area of the country.
- Basin States in India: Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, West Bengal, Uttarakhand, Haryana, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh and the UT of Delhi.
- Passing States: Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal.
- Enter Plain: At Haridwar and is joined by the Yamuna at Prayagraj (Allahabad).
- Total Length: 2,525 km.
- Important Towns: Haridwar, Kanpur, Soron, Kannauj, Allahabad, Varanasi, Patna, Ghazipur, Bhagalpur, Mirzapur, Ballia, Buxar, Saidpur, and Chunar.
Panch Prayag
| Prayags | Confluence of Rivers |
| Devaprayag | confluence of Bhagirathi river and Alaknanda River. |
| Rudraprayag | confluence of Mandakini river and Alaknanda river |
| Nandaprayag | confluence of Nandakini river and Alaknanda river. |
| Karnaprayag | confluence of Pindar river and Alaknanda river. |
| Vishnuprayag | confluence of Dhauliganga river and Alaknanda river. |

Himalayan Tributaries of Ganga
- Alaknanda River
- Origin: It rises at the confluence and feet of the Satopanth and Bhagirath glaciers in Uttarakhand.
- Confluence: It meets the Bhagirathi River at Devprayag after which it is called the Ganga.
- Tributaries: Its main tributaries are the Mandakini, Nandakini, and Pindar rivers.
- Pilgrimage Site: The Hindu pilgrimage centre of Badrinath and the natural spring Tapt Kund lie along the banks of the Alaknanda River.
- Bhagirathi River
- Origin: It rises at the foot of Gangotri Glacier, at Gaumukh, at an elevation of 3892m at Uttarakhand.
- Dhauliganga River
- Origin:It originates from Vasundhara Tal, perhaps the largest glacial lake in Uttarakhand.
- Confluence
- Dhauliganga is joined by the Rishiganga river at Raini.
- It merges with the Alaknanda at Vishnuprayag
- Project: Tapovan Vishnugad Hydro Power Project is being constructed on the Dhauliganga.
- Rishiganga River
- Origin: It springs from the Uttari Nanda Devi Glacier on the Nanda Devi Mountain.
- Fed by: Dakshini Nanda Devi Glacier.
- Passing Protected Area: It flows through the Nanda Devi National Park and merges into the Dhauliganga River
Left Bank Tributaries of Ganga River in Ganga Plain
- Ramganga River
- Origin: Ramganga River originates in the southern slopes of Dudhatoli Hill in Uttarakhand.
- Passing Region: It drains the southwestern region of the Kumaun.
- Passing Protected Area: It also flows through the dun valley of Corbett National Park.
- Confluence: It meets the Ganga near Kannauj.
- Gomati River
- Origin: It originates from Gomat Taal, Pilibhit in Uttar Pradesh.
- Confluence: Meets the Ganges River in Ghazipur.
- Pilgrimage Site: At the Sangam of Gomti and Ganga, the famous Markandey Mahadeo temple is situated.
- Ghaghariya River
- Origin
- The Ghagra originates in the glaciers of Mapchachungo.
- It is a transboundary perennial river originating from the Tibetan plateau near Lake Mansarovar.
- Associated River: It is a major left-bank tributary of the Ganga and joins it at Chhapra in Bihar.
- Tributaries: Rapti, Chhoti Gandak, Sharda, and Sarju are the major tributaries of this river.
- Origin
- Gandak River
- Origin: It is formed by the union of the Kali and Trisuli rivers, which rise in the Great Himalayan Range in Nepal.
- In Plain: It enters the Ganga river opposite to Patna in a place called Sonepur.
- Burhi Gandak River
- Origin: Originates from Chautarva Chaur near Bisambharpur in the district of West Champaran district of Bihar.
- Associated River: It flows parallel to and east of the Gandak River in an old channel.
- Kosi River
- Other Name
- Also called Saptakoshi for its 7 Himalayan tributaries.
- It is also termed as “The Sorrow of Bihar”.
- Type of Drainage: It is an antecedent transboundary river flowing through Nepal and India.
- Fact: The highest peak in the world, Mt. Everest, and the Kanchenjunga are situated in the Kosi catchment.
- Other Name
Right Bank Tributaries of Ganga River in Ganga Plain
- Yamuna River System
- Origin: It originates from the Yamunotri Glacier on the southwestern slopes or Bandarpoonch Peak in the Mussoorie range of the lower Himalayas.
- Passing States: Flows through the states of Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and Haryana. It then enters Delhi and merges with the Ganga near Prayagraj.
- Tributary: It is the largest tributary of the Ganga in the northern plains.
- Geographical Features: It creates the highly fertile alluvial Yamuna-Ganges Doab region between itself and the Ganges in the Indo-Gangetic plain.
- Urban Centers: The cities of Bhagpat, Delhi, Noida, Mathura, Agra, Firozabad, Etawah, Hamirpur, and Allahabad lie on its banks.
- Major Tributaries are
- Chambal River: Chambal river originates from Janapao Hills of the Vindhya range. Major dams are Gandhi Sagar dam, Rana Pratap Sagar dam, Jawahar Sagar Dam and the Kota Barrage. The region is known for badland topography.
- Banas River: Originates in the Aravalli Range in Rajasthan.
- Kali Sindh: Flows in the Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh and joins the Chambal River in Rajasthan.
- Ken River: The Ken River originates from the slopes of the Kaimur Range in Madhya Pradesh and merges with the Yamuna near Fatehpur in Uttar Pradesh.
- Betwa River: Rises in the Vindhya Range in Madhya Pradesh and merges with Yamuna Rivers in Hamirpur town in Uttar Pradesh
- Sindh River: The Sindh river originates from the Malwa Plateau.
- Son River
- Origin: Originates near Amarkantak hills in Madhya Pradesh
- Tributary: It joins the Ganga near Patna in Bihar.
