Mineral Resources
- Definition:
- Minerals are naturally occurring, solid, inorganic substances with a crystal structure.
- There are over 2,000 minerals, most of which are inorganic, but some organic materials like gold and sulfur also exist.
- Categories of Mineral Resources:
- Metallic Minerals:
- Contain metal elements (e.g., iron, copper, gold).
- When melted, they form new products.
- Examples: Iron ore, copper, gold, silver, etc.
- Subdivided into ferrous (contains iron) and non-ferrous (does not contain iron).
- Non-Metallic Minerals:
- Do not contain metal elements.
- Do not form new products when melted.
- Examples: Mica, limestone, graphite, coal, petroleum.
- Can be organic (fossil fuels) or inorganic.
- Metallic Minerals:
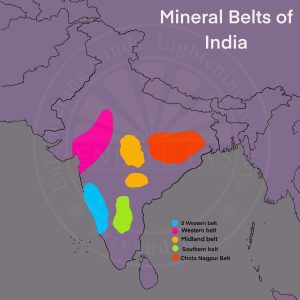
Mineral Belts in India
- Northern Belt: Includes regions like Chhota Nagpur Plateau, Assam (petroleum and lignite).
- Central Belt: Includes Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra with iron ore and limestone.
- South Eastern Region: Includes Karnataka (iron ore), Andhra Pradesh (mica), Tamil Nadu (lignite coal).
- South Western Region: Includes Goa (iron ore), Karnataka (high mineral reserves).
- North Western Region: Includes Rajasthan and Gujarat (salt, petroleum).