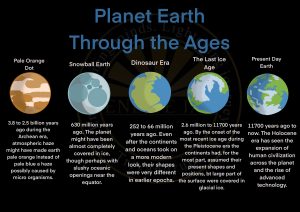
Evolution of Earth
- The earth broke off about 4.5 billion years ago with an explosion.
- It was a burning hot white mass of gas and dust.
- Over a long period, dust and gas gradually condensed to form solid rock.
- Such condensation and shrinking made the earth heat up so much that the rock melted into a gluey liquid.
- After millions of years, the outer surface of the earth or the earth’s crust cooled and formed hard rock again, just as melted wax solidifies upon cooling.
- The interior of the earth is still very hot.
- The crust of the earth was formed from the cooling and hardening of the molten matter and hot gases.
- With the cooling of the earth, the crust hardened and formed the land.
- Cooling of the earth also condensed water vapour into liquid water filling the depressions to form seas.
Basics of Earth
- Earth is the only known planet where life exists.
- Its surface area is covered with two-thirds of water and so it is called the blue planet.
- Earth is the third planet from the sun, the densest planet in the solar system, the largest of the solar system’s four terrestrial planets.
- It is slightly flattened at the poles, that is why its shape is described as a Geoid.
- Our Earth is around 4.5 billion years old.
- Earth revolves around the Sun once every 365.25 days – this is known as one Earth year. But every four years, February has 29 days instead of 28, so there are 366 days in the year. This is called a leap year.
- The surface of Earth is covered by water, around 71%. Only 29% of Earth’s surface is covered by land.
- The atmosphere of Earth is divided into 6 layers – the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere, and ionosphere.
- Earth has only one satellite – the Moon.
