Rotation
- Earth rotates along its axis from west to east.
- It takes approximately 24 hrs to complete one rotation.
- Earth rotates in a counter-clockwise direction.
- Days and nights occur due to rotation of the earth.
- The circle that divides the day from night on the globe is called the circle of illumination.
- Earth rotates on a tilted axis. Earth’s rotational axis makes an angle of 23.5° with the normal.
- It makes an angle of 66.5° with the orbital plane.
- Effects
- Rotation creates a diurnal cycle of light and darkness, temperature, and humidity changes.
- Rotation requires the creation of standardised time zones. There are 24, one for each hour of the earth’s rotation.
- Rotation causes the tides.
- Rotation causes a deflection of ocean and air currents.

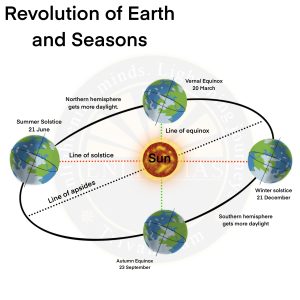
Revolution
- The second motion of the earth around the sun in its orbit is called revolution.
- It takes 365¼ days (one year) to revolve around the sun.
- Six hours saved every year are added to make one day (24 hours) over a span of four years. This surplus day is added to the month of February.
- Thus every fourth year, February has 29 days instead of 28 days. Such a year with 366 days is called a leap year.
- The closest Earth gets to the Sun each year is at perihelion (147 million km) around January 3rd and the furthest is at aphelion (152 million km) on July 4th.
- During the Northern Hemisphere summer, the North Pole points toward the Sun, and in the Northern Hemisphere winter, the North Pole is tilted away from the Sun.
- Effects
- Occurrence of various seasons (spring, summer, autumn and winter).
Solstices
|