Super Volcanoes
- A supervolcano is a large volcano in which the volume of magma deposits that can erupt to the surface is greater than 1,000 cubic km.
- Supervolcanoes occur when a large volume of magma accumulates under the lithospheric plate but is unable to break through it.
- Over time, the pressure keeps building up until the plate can no longer contain the pressure, resulting in an eruption.
- This can occur at hotspots or subduction zones.
- A supervolcanic super-eruption can cause a small-scale or regional extinction event.
Submarine Volcanoes
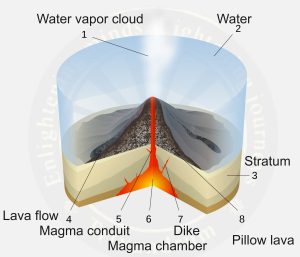
- Submarine volcanoes are erupting basaltic lavas and new crust material is actively formed with substantial piles of pillow lavas.
- Submarine volcanoes are underwater vents or fissures in the Earth’s surface from which magma can erupt.
- Many submarine volcanoes are located near areas of tectonic plate formation, known as mid-oceanic ridges.
- The volcanoes at mid-oceanic ridges alone are estimated to account for 75% of the magma output on Earth.
- For example – Fukutoku-Okanoba Submarine Volcano