Ripples
- Low-speed winds deposit the particles in the shape of waves, which are known as sand ripples.
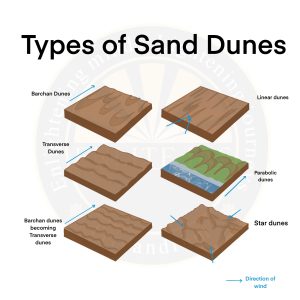
Sand Dunes
- Velocity of wind carrying sand decreases when it faces some obstacle and therefore wind starts depositing the sand particles on the spot of the obstacle which results in the formation of sand dunes.
- Sand Dunes are classified into
- Barchan
- Half-moon and crescent shaped sand dunes are known as Barchans.
- These are convex on the windward side and steeper and concave on the leeward side.
- Self or Longitudinal Sand Dunes
- These sand dunes are generally oriented in a direction parallel to prevailing winds but when the dunes blow out, sand gets deposited in parallel forms.
- Barchan
Loess Plains
- Winds deposit light and soft soil over a large area like a blanket, these are known as plains of Loess.
- Loess is found in China, Europe, North America, South America and Africa.
Playas
- These are temporary lakes in the desert.
- Formed in arid or semi-arid areas by intermittent streams flowing into depressions.
- Contain a high percentage of salts due to high evaporation & lower precipitation.
Bajada
- Depositional features made up of alluvial material lay down by intermittent streams.
- Bajada is formed by the coalescence of alluvial fans.
- These fan-shaped deposits form from the deposition of sediments by a stream from the upland region onto flat land at the base of a mountain.
- Bajadas are common in arid areas where a large quantity of sediment is deposited by flash floods.
Pediment
- An erosional plain of low relief formed in an arid or semi arid region at the base of a receding mountain front.
- They are gently inclined rocky floors close to the mountains at their foot with or without a thin cover of debris.
- They form through the erosion of the mountain front through a combination of lateral erosion by streams and sheet flooding.
- Through parallel retreat of slopes, the pediments extend backwards at the expense of the mountain front.
- Gradually, the mountain gets reduced leaving an inselberg which is a remnant of the mountain.
- That’s how the high relief in desert areas is reduced to low featureless plains called pediplains.


