Permanent Winds or Primary Winds or Prevailing Winds or Planetary Winds
- What is it?
- Planetary or permanent winds blow from high-pressure belts to low-pressure belts in the same direction throughout the year.
- They blow over a vast area of continents and oceans
- Types
- Easterlies
- The winds that blow from sub-tropical high pressure areas towards equatorial low pressure areas called trade winds.
- These are confined to a region between 30°N and 30°S throughout the earth’s surface.
- They flow as the north-eastern trades in the northern hemisphere and the south-eastern trades in the southern hemisphere.
- As the trade winds tend to blow mainly from the east, they are also known as the Tropical easterlies.
- Trade winds are descending and stable in areas of their origin (sub-tropical high-pressure belt), and as they reach the equator, they become humid and warmer after picking up moisture on their way.
- The trade winds from two hemispheres meet at the equator, and due to convergence they rise and cause heavy rainfall.
- Westerlies
- The winds that move poleward from the sub-tropical high pressure in the northern hemisphere are deflected to the right and thus blow from the south west.
- These in the southern hemisphere are deflected to the left and blow from the north-west, so these winds are called westerlies.
- The westerlies are best developed between 40° and 65°S latitudes. These latitudes are often called Roaring Forties, Furious Fifties, and Shrieking Sixties.
- Polar Easterlies
- The Polar easterlies are dry, cold prevailing winds blowing from north-east to south-west direction in Northern Hemisphere and south-east to the north-west in Southern Hemisphere.
- They blow from the polar high-pressure areas of the sub-polar lows
- Easterlies
Periodic Winds
- These winds change their direction with change in season.
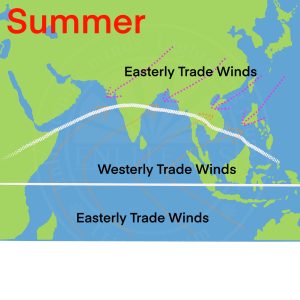
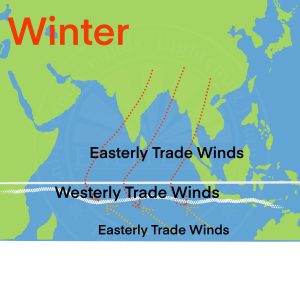
- Monsoon Winds
- The word ‘Monsoon’ has been derived from the Arabic word ‘Mausim’ meaning season.
- The winds that reverse their direction with the change of seasons are called monsoon winds.
- During summer the monsoon winds blow from sea towards land and during winter from land towards seas.
- India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Myanmar(Burma), Sri Lanka, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, South-east Asia, North Australia, China and Japan are important regions where monsoon winds are prevalent.
- Monsoon Winds
-
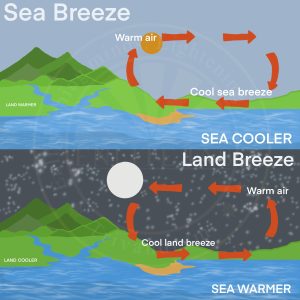
- Land Breeze and Sea Breeze
- Sea Breeze
- This process takes place for the duration of the day.
- Both the sea and the land surface are heated up by the sun.
- The sea heats up slower than the land because it has a much higher heat capacity.
- Thus, the temperature over the land surface increases, in turn, heating up the surrounding air.
- Expansion occurs in the less dense warm air and an area over the land having low pressure is developed.
- At the same time on the top of the sea, a high-pressure area develops.
- Due to the difference in pressure, the air flows from the high pressure over the sea to the low pressure over the land.
- This flow of air from the sea to the land is termed as the sea breeze.
- Sea Breeze
- Land Breeze and Sea Breeze
-
-
- Land Breeze
- This process takes place for the duration of the night and the above-mentioned process gets reversed.
- Both the land and the sea start cooling down when the sunsets.
- As the heat capacity of the land is different from the sea it cools down quicker.
- Thus, a low-pressure situation develops over the sea as the temperature above it is higher when compared to the land.
- Due to this, the air flows from the land to the sea which is termed the land breeze.
- Land Breeze
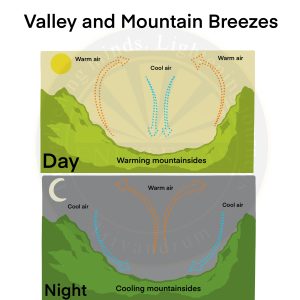
- Valley Breeze and Mountain Breeze
- Valley Breeze
- During day time valley region receives more insolation and radiates more terrestrial radiation heating up the air present on the valley surface.
- Air on heating loses its density and moves up the mountain surface causing valley breeze.
- Mountain Breeze
- During night, air on the mountain surface cools, gains density and seeps down to the valley floor causing mountain breeze.
- Valley Breeze
-
Local Winds
- Hot Winds
| Hot Wind | Features |
| Loo |
|
| Foehn |
|
| Chinook |
|
| Santa Ana |
|
| Sirocco |
|
| Harmattan |
|
- Cold Winds
| Cold Wind | Features |
| Mistral |
|
| Bora |
|
| Blizzard |
|
| Pampero |
|