Desert
- Desert – A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life.
- About 1/5 of the world’s land is made up of deserts.
- Almost all the deserts are confined within 15 degree – 30 degree parallels to N-S of the equator known as trade wind deserts or tropical deserts.
- They lie in the trade wind belt on the western parts of the continents.
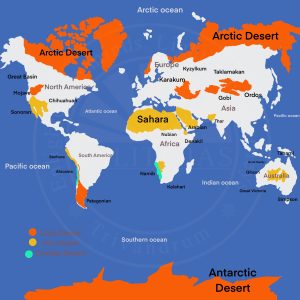
Distribution of Deserts in the World
Mechanisms Involved in the Formation of Deserts
- Deflation
- Involves lifting and blowing away loose materials from the ground.
- Blowing capacity depends largely on the size of the material lifted from the surface.
- Finer dust and sands may be removed miles away from their place of origin & may get deposited even outside the desert margins.
- Deflation results in the lowering of the land surface to form large depressions called ‘Deflation Hollows’.
- Abrasion
- It is the sandblasting of rock surfaces by the wind when they hurl sand particles against them.
- This results in rock surfaces being scratched, polished & worn away.n
- Abrasion is most effective near the base of the rocks, where the amount of material the wind is able to carry is greatest.
- This explains why telegraphic poles in the deserts are protected by covering of metal for a foot or two above the ground.
- Attrition
- When wind-borne particles roll against one another in the collision, they wear each other away.
- Hence their sizes are greatly reduced and grains are rounded into millet seed sands.

