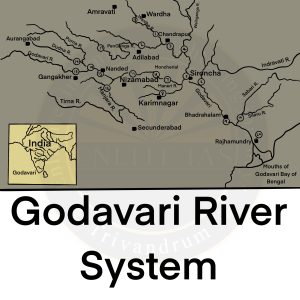
Basics
- Fact: The Godavari River is the largest river in Peninsular India.
- Other Name: It is known as the Dakshin Ganga or Vridha Ganga.
- Source: It rises from Trimbakeshwar located in the Western Ghats in Nashik, Maharashtra.
- Basin States: Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha in addition to smaller parts of Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Borders: Satmala hills, the Ajanta range, and the Mahadeo hills on the north, the Eastern Ghats on the south and the east, and the Western Ghats on the west.
- Dams: Sri Ram Sagar project, Pichavaram project, Polavaram project.
- Tributaries
- Left Bank: Dharna, Penganga, Wainganga, Wardha, Pranahita, Pench, Kanhan, Sabari, and Indravati rivers.
- Right Bank: Pravara, Mula, Manjra, Peddavagu, and Maner rivers.
Major Tributaries
- Manjra River
- It originates in the Balaghat range, near Ahilya Nagar (old name – Ahmednagar) in Maharashtra.
- Manjra River flows through Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Painganga River
- It originates in the Ajanta ranges of Maharashtra.
- It then flows along the state border between Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh.
- It passes through the Painganga Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Sahastrakund waterfalls are situated on it.
- Wardha River
- It originates in the Satpura range in Madhya Pradesh and flows through Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
- Indravati River
- It originates from the Eastern Ghats in Kalahandi in Odisha.
- It also forms the boundary between Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh.
- Known as the lifeline of the Bastar district.
- Chitrakoot Falls is located on the Indravati River.