What is it?
- Ecological succession is the steady and gradual change in a species of a given area with respect to the changing environment.
- The succession moves towards achieving an equilibrium in the environment.
- In some environments, succession reaches a climax, which produces a stable community dominated by a small number of prominent species. This state of equilibrium, called the “climax community”.
- There are two types of succession that primary and secondary succession. Both the primary and secondary succession goes through a number of intermediate stages to reach a climax stage. These intermediate stages are known as seral stages.
Types
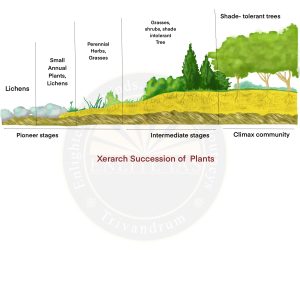
- Primary Succession
- This succession starts in lifeless areas such as the regions devoid of soil or the areas where the soil is unable to sustain life.
- For Example – Initially, the earth was only made up of rocks. These rocks were broken down by microorganisms and eroded to form soil. The soil then becomes the foundation of plant life. These plants help in the survival of different animals and progress from primary succession to the climax community.

- Secondary Succession
- It occurs in areas where a community that previously existed has been removed; it is typified by smaller-scale disturbances that do not eliminate all life and nutrients from the environment.
- For Example: Suppose a climax community gets destroyed by fire. Then it gets recolonized after the destruction. This is known as secondary ecological succession



