Basics
- The interaction of matter and temperature generates these forces or movements inside the earth’s crust.
- These internal forces lead to vertical and horizontal movements and result in subsidence, land upliftment, volcanism, faulting, folding, earthquakes, etc.
- The energy emanating from within the earth is the main force behind endogenic geomorphic processes.
- This energy is mostly generated by radioactivity, rotational and tidal friction and primordial heat from the origin of the earth.
Classification of Endogenic Forces
- Diastrophism
- Diastrophic forces can be defined as the pressure that is created due to the motion of the solid material on the earth’s surface.
- Diastrophism is the general term applied to slow bending, folding, warping, and fracturing
- They include:
- Orogenic Processes
- It involve Horizontal Movements
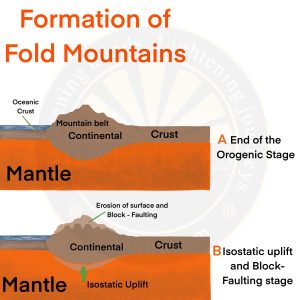
- Orogenic processes involve mountain building through severe folding and affects long and narrow belts of the earth’s crust.
- In the process of orogeny, the crust is severely deformed into folds.
- Main forces acting are tension and compression that create fissures and folds respectively.
- Fold mountains like Andes are created through this process.
- Orogenic Processes

-
-
- Epeirogenic Processes
- It is a vertical movement.
- Epeirogenic processes involve uplift or warping of large parts of the earth’s crust.
- Epeirogenic or continent forming movements act along the radius of the earth; therefore, they are also called radial movements.
- Their direction may be towards (subsidence) or away (uplift) from the centre.
- Example for subsidence – Rann of Kachchh region.
- Example for Uplift – Coringa near the mouth of the Godavari.
- Epeirogenic Processes
-
- Sudden Movements
- Sudden geomorphic movements occur mostly at the lithospheric plate margins (tectonic plate margins).
- The plate margins are highly unstable regions due to pressure created by pushing and pulling of magma in the mantle (convection currents).
- These movements cause considerable deformation over a short period.
- For example – earthquake, and volcanism.

