Why in the news?
- Scientists have engineered a new CRISPR protein called GlowCas9.
GlowCas9
- What is it?: A bioluminescent variant of Cas9 engineered by fusing Cas9 with a split nano-luciferase enzyme derived from deep-sea shrimp proteins.
- Developed by: Developed by scientists at Bose Institute, Kolkata (DST)
- Key Features:
- Real-time Visualization owing to bioluminescence.
- More thermostable and structurally stable than conventional Cas9.
- Increased precision in Gene editing
- Offers possibilities for safe, non-transgenic crop improvement.
- Demonstrates potential for targeted and customizable DNA repair.
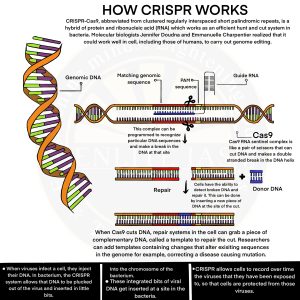
CRISPR-Cas9
- Full-Form: Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats – Cas9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9).
- Function: A precise, efficient, and versatile gene-editing tool.
- Applications:
- Medicine:
- Treats genetic disorders (e.g., sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis).
- Advances cancer research (e.g., CAR-T therapy, tumor models).
- Corrects inherited mutations (e.g., eye disorders via stem cells).
- Agriculture:
- Enhances crop traits (e.g., disease resistance, higher yield).
- Edits plant genomes (e.g., sweeter tomatoes using CRISPR variants like Cas12, Cas13).
- Research:
- Identifies gene functions.
- Develops CRISPR-based diagnostics for pathogens.
- Medicine:
- Advantages
- Precision: Targets specific DNA sequences.
- Efficiency: Faster and cheaper than traditional methods.
- Versatility: Applicable across species.
- Challenges
- Ethical Concerns: Germline editing and “designer babies.”
- Off-Target Effects: Risk of unintended genome changes.
- Patent Disputes: Restricts accessibility (e.g., CRISPR patents held by Broad Institute).
- Cost and Accessibility: Limited reach in low-resource settings.
- Notable Milestones:
- Nobel Prize (2020): Dr. Jennifer Doudna and Dr. Emmanuelle Charpentier.
Source: PIB
