Basics
- The Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilization, was one of the world’s oldest urban civilizations, flourishing in what is now modern-day India and Pakistan between 3300 and 1300 BCE. The Indus River, which flows through the region where the civilization’s key ruins were unearthed, inspired its name.

Pic Credit- Wikimedia Commons
- First Urban Civilisation of South Asia
- Mesopotamian and Egyptian civilizations are contemporaries to Indus Valley Civilisation.
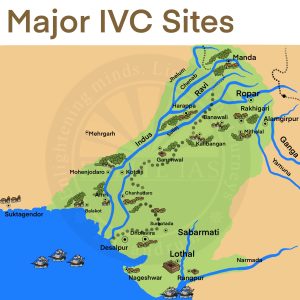
Important IVC sites
|
Site |
Location |
Important Findings |
|
Harappa |
Situated on the banks of the river Ravi in Punjab (Pakistan). |
|
|
Mohenjo-Daro (Also called Mound of Dead) (UNESCO World Heritage Site) |
Situated on the Bank of River Indus in Punjab (Pakistan) |
|
|
Sutkagendor |
In southwestern Balochistan province, Pakistan on the Dast river |
|
|
Chanhudaro |
Sindh (Pakistan) on the Indus River |
|
|
Amri |
Rajasthan on the bank of the Ghaggar River |
|
|
Kalibangan |
Rajasthan on the bank of the Ghaggar river |
|
|
Lothal |
Gujarat on the Bhogva River near Gulf of Cambay |
|
|
Surkotada |
Gujarat |
|
|
Banawali |
Haryana |
|
|
Dholavira (UNESCO World Heritage Site) |
Gujarat in Rann of Kachchh |
|
|
Rakhigarhi |
Haryana |
|
|
Ropar (The first site to be excavated after independence.) |
On the banks of River Sutlej in Punjab, India |
|
|
Alamgirpur |
Meerut, Uttar Pradesh on the banks of Yamuna – Easternmost site of IVC. |
|
|
Mehrgarh |
Pakistan |
|
|
Kot Diji |
Pakistan |
|
|
Daimabad (southernmost site of IVC) |
Maharashtra |
|
|
Mand (Northernmost site) |
Jammu and Kashmir |
Phases of Harappan Civilisation
- Early/Pre-Harappan Phase (3500 BCE-2500 BCE)
- This phase is also linked to the Hakra Phase, which is found in the Ghaggar-Hakra River Valley.
- This era includes the oldest specimens of the Indus Script, which date back to 3000 BCE.
- This period was most likely characterised by centralised authority and a more urban way of life.
- During the Early Harappan Phase, trade networks were also created.
- Moreover, evidence of crop cultivation such as peas, sesame seeds, dates, cotton, and so on exists throughout this time.
- Mature Harappan Phase (2500 BCE – 1800 BCE)
- Urban centres like Harappa, Mohenjo-Daro, etc developed.
- Late Harappan Phase (1800 BCE – 1500 BCE)
- Gradual decline of IVC.


