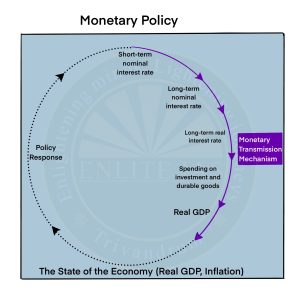
Monetary Policy Transmission
- It refers to the process by which the Central Bank’s actions to control the money supply (such as a change in the Repo Rate) are transmitted to the final objectives of stable inflation and growth.
- It involves the entire process starting from the change in the Policy Rate ( such as the Repo Rate) by the RBI, its response in the financial markets, and the ultimate effect on businesses and households.
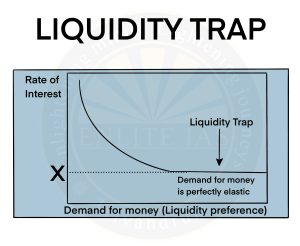
Liquidity Trap
- Liquidity Trap is an adverse economic situation that occurs when consumers and investors prefer to hold onto their cash rather than spend or invest them, even when interest rates are low.
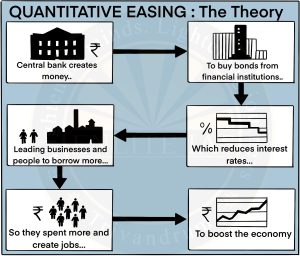
Quantitative Easing (QE)
- Quantitative Easing (QE) refers to the Central Bank’s action of purchasing securities from the open market to reduce interest rates and increase the money supply.
- It is aimed to create new bank reserves, providing banks with more liquidity, and encouraging lending and investment.
Sterilisation
- It refers to the process by which the RBI takes away money from the banking system to neutralise the fresh money that enters the system.
