- Origin and Occurrence
- Petroleum is an organic liquid found in sedimentary basins, seas, and shallow depressions, primarily in anticlines and fault traps formed over millions of years.
- Oil reservoirs need porosity, permeability, and impermeable caps to retain oil.
- Major Oilfields in India:
- Northeastern India: Assam (Digboi, Naharkatia), Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Western India: Gujarat (Ankleshwar, Kalol, Mehsana), Maharashtra (Mumbai High, Bassein).
- Rajasthan: Barmer (Mangla, Bhagyam, Aishwarya).
- Offshore Fields: Mumbai High, Bassein (Mumbai), Krishna-Godavari basin (East Coast).
- Refining and Transport:
- India’s first refinery was in Digboi (1901). Major refineries are in Mumbai, Gujarat, and Assam.
- Pipeline systems like Salaya-Mathura, Mundra-Panipat transport crude oil to refineries.
- Petroleum Use: Petroleum is key for transportation, power generation, lubricants, and petrochemical products.
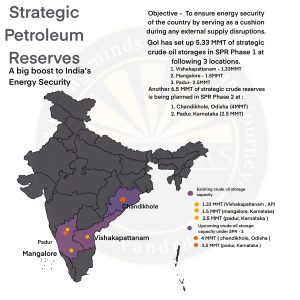
- Strategic Petroleum Reserves:
- Reserves are located at Visakhapatnam, Mangaluru, and Padur.
- Underground storage is economical and secure for crude oil stockpiling