Why in the news?
- Researchers at University College London successfully demonstrated that amino acids can spontaneously and selectively attach to RNA molecules.
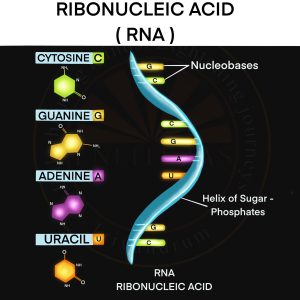
RNA Molecule
- What is it?: RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) is a nucleic acid that plays a central role in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes.
- Features:
- It is usually single-stranded (unlike double-stranded DNA).
- Composed of ribose sugar, phosphate backbone, and nitrogenous bases (Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine).
- Types of RNA:
- mRNA (Messenger RNA):
- Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes.
- Acts as a template for protein synthesis.
- tRNA (Transfer RNA):
- Transfers specific amino acids to ribosomes.
- Decodes mRNA codons into amino acids.
- rRNA (Ribosomal RNA):
- Structural and functional components of ribosomes.
- Catalyzes peptide bond formation (acts as a ribozyme).
- Other RNAs (Regulatory RNAs):
- snRNA (small nuclear RNA): Involved in RNA splicing.
- miRNA, siRNA: Regulate gene expression (RNA interference).
- lncRNA (long non-coding RNA): Chromatin modification & transcriptional regulation.
- mRNA (Messenger RNA):
- Key Concepts regarding RNA:
- Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: DNA → RNA → Protein.
- Reverse Transcription: Some viruses (e.g., HIV, retroviruses) use RNA as genetic material, converting RNA → DNA via reverse transcriptase.
- RNA World Hypothesis: Suggests early life on Earth may have relied solely on RNA for both genetic information storage and catalysis.
- Significance of RNA:
- Medical: Target for therapies (RNAi, mRNA vaccines).
- Evolutionary Biology: Provides clues to life’s origin (RNA World).
- Biotechnology: CRISPR, synthetic biology, genetic engineering.
Amino Acids
- What are they?:
- Amino acids are organic compounds containing an amino group (–NH₂), a carboxyl group (–COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a variable R-group (side chain) attached to a central carbon (α-carbon).
- They are the building blocks of proteins, essential for growth, repair, metabolism, and signaling in living organisms.
- Classification: Based on Nutritional Requirement;
- Essential Amino Acids (9 in humans): Must be obtained from diet
- Non-Essential Amino Acids: Synthesized in the body
- Conditionally Essential: Required in stress/illness
- Functions of Amino Acids:
- Structural: Form proteins (collagen, keratin).
- Metabolic: Involved in enzymatic reactions, hormones (e.g., thyroxine from tyrosine).
- Energy: Serve as energy source during fasting/starvation.
- Signaling: Neurotransmitters (e.g., glutamate, GABA derived from glutamate).
- Immune role: Glutamine, arginine critical for immunity.
