- Other Name: It is also called the expanding universe hypothesis.
- About Theory
- Discovery: Edwin Hubble, in 1920, provided evidence that the universe is expanding.
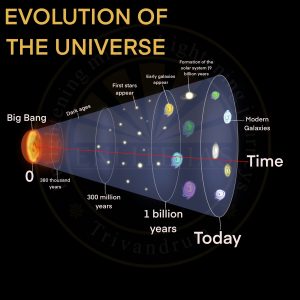
- Period: Took place 13.7 billion years ago.
- Findings
- Galaxies move further and further apart. Similarly, the distance between the galaxies is also found to be increasing, and thereby, the universe is considered to be expanding.
- Scientists believe that though the space between the galaxies is increasing, observations do not support the expansion of galaxies.
- Stages of Development
- In the beginning, all matter forming the universe existed in one place in the form of a “tiny ball” (singular atom) with an unimaginably small volume, infinite temperature, and infinite density.
- At the Big Bang the “tiny ball” exploded violently leading to a huge expansion.
- The expansion continues even to the present day.
- As it grew, some energy was converted into matter.
- There was particularly rapid expansion within fractions of a second after the bang.
- Thereafter, the expansion has slowed down. Within the first three minutes of the Big Bang event, the first atom began to form.
- Within 300,000 years from the Big Bang, the temperature dropped to 4,500K (Kelvin) and gave rise to atomic matter.
- The universe became transparent.